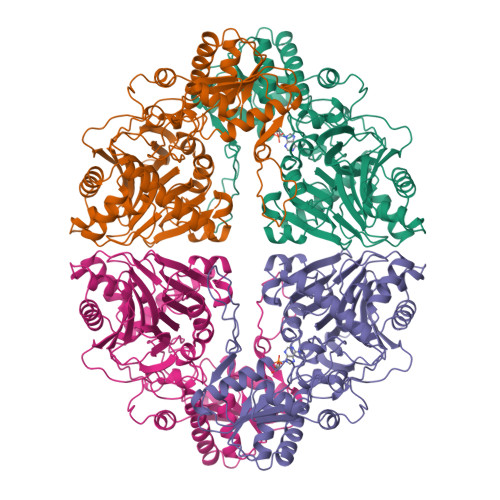
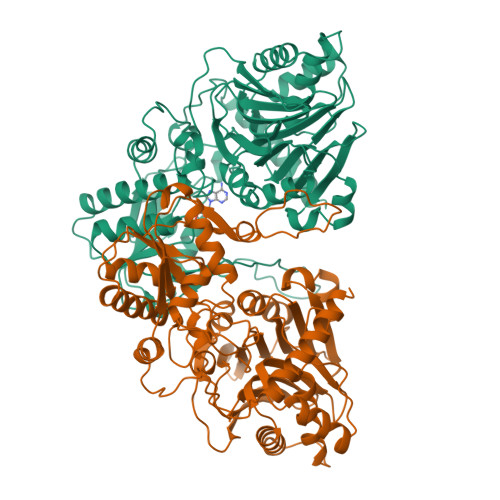
Crystal structure of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase from Escherichia coli.
Muchmore, C.R., Krahn, J.M., Kim, J.H., Zalkin, H., Smith, J.L.(1998) Protein Sci 7: 39-51
- PubMed: 9514258
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560070104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ECF, 1ECJ - PubMed Abstract:
Crystal structures of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) amidotransferase from Escherichia coli have been determined to 2.0-A resolution in the absence of ligands, and to 2.5-A resolution with the feedback inhibitor AMP bound to the PRPP catalytic site. Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase (GPATase) employs separate catalytic domains to abstract nitrogen from the amide of glutamine and to transfer nitrogen to the acceptor substrate PRPP. The unliganded and AMP-bound structures, which are essentially identical, are interpreted as the inhibited form of the enzyme because the two active sites are disconnected and the PRPP active site is solvent exposed. The structures were compared with a previously reported 3.0-A structure of the homologous Bacillus subtilis enzyme (Smith JL et al., 1994, Science 264:1427-1433). The comparison indicates a pattern of conservation of peptide structures involved with catalysis and variability in enzyme regulatory functions. Control of glutaminase activity, communication between the active sites, and regulation by feedback inhibitors are addressed differently by E. coli and B. subtilis GPATases. The E. coli enzyme is a prototype for the metal-free GPATases, whereas the B. subtilis enzyme represents the metal-containing enzymes. The structure of the E. coli enzyme suggests that a common ancestor of the two enzyme subfamilies may have included an Fe-S cluster.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA.