Apoprotein structure in the LH2 complex from Rhodopseudomonas acidophila strain 10050: modular assembly and protein pigment interactions.
Prince, S.M., Papiz, M.Z., Freer, A.A., McDermott, G., Hawthornthwaite-Lawless, A.M., Cogdell, R.J., Isaacs, N.W.(1997) J Mol Biology 268: 412-423
- PubMed: 9159480
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.0966
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
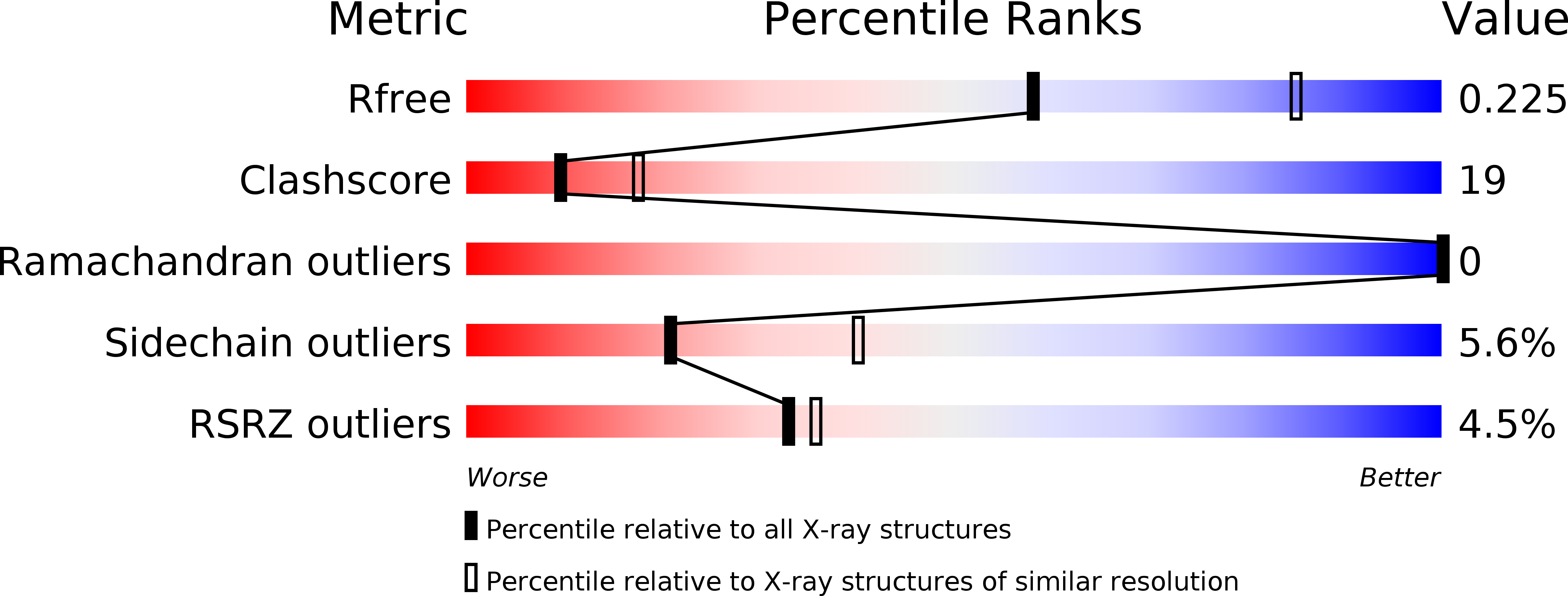
1KZU - PubMed Abstract:
The refined structure of the peripheral light-harvesting complex from Rhodopseudomonas acidophila strain 10050 reveals a membrane protein with protein-protein interactions in the trans-membrane region exclusively of a van der Waals nature. The dominant factors in the formation of the complex appear to be extramembranous hydrogen bonds (suggesting that each apoprotein must achieve a fold close to its final structure in order to oligomerize), protein-pigment and pigment-pigment interactions within the membrane-spanning region. The pigment molecules are known to play an important role in the formation of bacterial light-harvesters, and their extensive mediation of structural contacts within the membrane bears this out. Amino acid residues determining the secondary structure of the apoproteins influence the oligomeric state of the complex. The assembly of the pigment array is governed by the apoproteins of LH2. The particular environment of each of the pigment molecules is, however, influenced directly by few protein contacts. These contacts produce functional effects that are not attributable to a single cause, e.g. the arrangement of an overlapping cycle of chromophores not only provides energy delocalisation and storage properties, but also has consequences for oligomer size, pigment distortion modes and pigment chemical environment, all of which modify the precise function of the complex. The evaluation of site energies for the pigment array requires the consideration of a number of effects, including heterogeneous pigment distortions, charge distributions in the local environment and mechanical interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Glasgow, UK.