Structure of Human Phytanoyl-CoA 2-Hydroxylase Identifies Molecular Mechanisms of Refsum Disease
McDonough, M.A., Kavanagh, K.L., Butler, D., Searles, T., Oppermann, U., Schofield, C.J.(2005) J Biological Chem 280: 41101-41110
- PubMed: 16186124
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507528200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2A1X - PubMed Abstract:
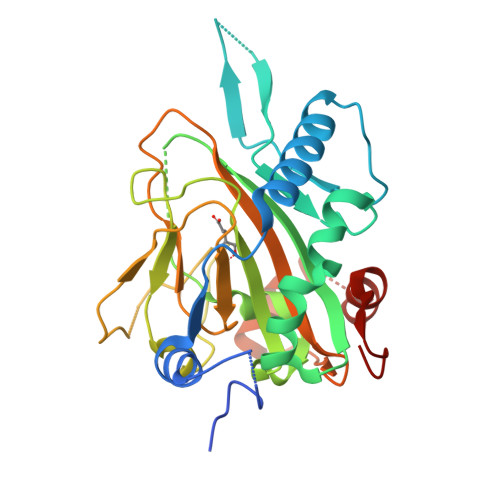
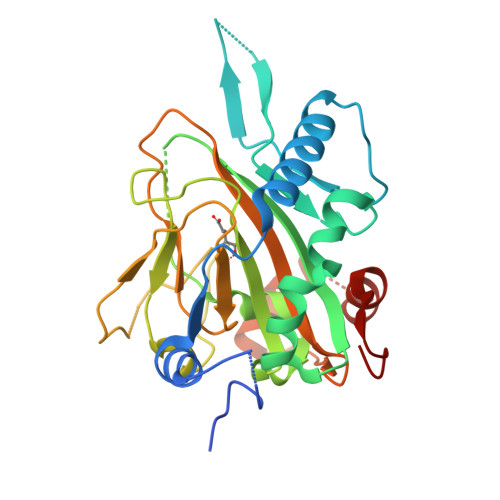
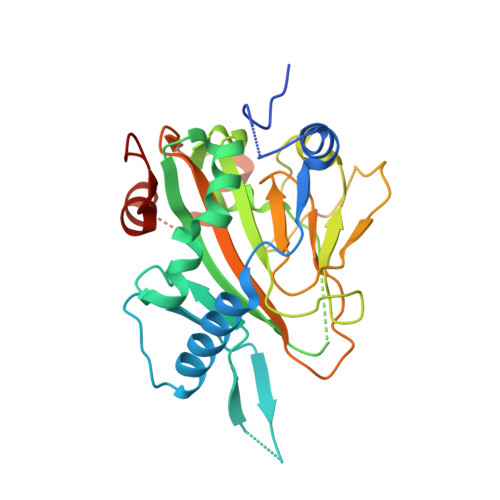
Refsum disease (RD), a neurological syndrome characterized by adult onset retinitis pigmentosa, anosmia, sensory neuropathy, and phytanic acidaemia, is caused by elevated levels of phytanic acid. Many cases of RD are associated with mutations in phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase (PAHX), an Fe(II) and 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent oxygenase that catalyzes the initial alpha-oxidation step in the degradation of phytenic acid in peroxisomes. We describe the x-ray crystallographic structure of PAHX to 2.5 A resolution complexed with Fe(II) and 2OG and predict the molecular consequences of mutations causing RD. Like other 2OG oxygenases, PAHX possesses a double-stranded beta-helix core, which supports three iron binding ligands (His(175), Asp(177), and His(264)); the 2-oxoacid group of 2OG binds to the Fe(II) in a bidentate manner. The manner in which PAHX binds to Fe(II) and 2OG together with the presence of a cysteine residue (Cys(191)) 6.7 A from the Fe(II) and two further histidine residues (His(155) and His(281)) at its active site distinguishes it from that of the other human 2OG oxygenase for which structures are available, factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor. Of the 15 PAHX residues observed to be mutated in RD patients, 11 cluster in two distinct groups around the Fe(II) (Pro(173), His(175), Gln(176), Asp(177), and His(220)) and 2OG binding sites (Trp(193), Glu(197), Ile(199), Gly(204), Asn(269), and Arg(275)). PAHX may be the first of a new subfamily of coenzyme A-binding 2OG oxygenases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Oxford Centre for Molecular Sciences and Department of Chemistry, University of Oxford, Mansfield Road, Oxford OX1 3TA, United Kingdom.