Complexes of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase 1 and pullulan model oligossacharides provide new insight into the mechanism for recognizing substrates with alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkages
Abe, A., Yoshida, H., Tonozuka, T., Sakano, Y., Kamitori, S.(2005) FEBS J 272: 6145-6153
- PubMed: 16302977
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05013.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D0F, 2D0G, 2D0H - PubMed Abstract:
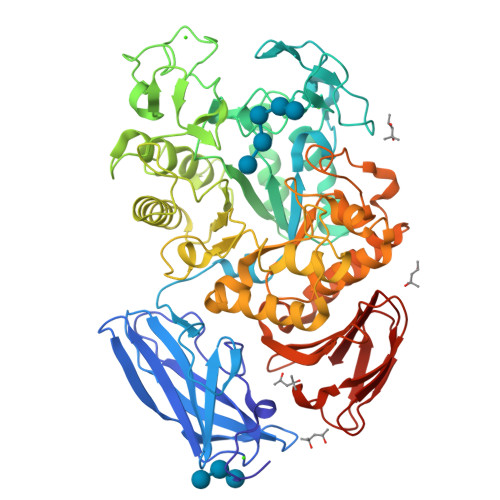
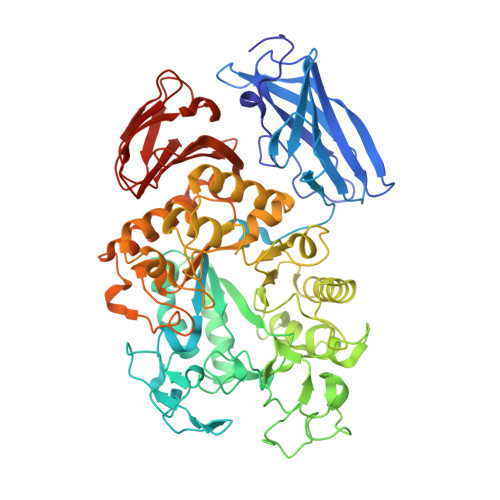
Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase 1 (TVAI) has unique hydrolyzing activities for pullulan with sequence repeats of alpha-(1,4), alpha-(1,4), and alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkages, as well as for starch. TVAI mainly hydrolyzes alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages to produce a panose, but it also hydrolyzes alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkages with a lesser efficiency. X-ray structures of three complexes comprising an inactive mutant TVAI (D356N or D356N/E396Q) and a pullulan model oligosaccharide (P2; [Glc-alpha-(1,6)-Glc-alpha-(1,4)-Glc-alpha-(1,4)]2 or P5; [Glc-alpha-(1,6)-Glc-alpha-(1,4)-Glc-alpha-(1,4)]5) were determined. The complex D356N/P2 is a mimic of the enzyme/product complex in the main catalytic reaction of TVAI, and a structural comparison with Aspergillus oryzaealpha-amylase showed that the (-) subsites of TVAI are responsible for recognizing both starch and pullulan. D356N/E396Q/P2 and D356N/E396Q/P5 provided models of the enzyme/substrate complex recognizing the alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkage at the hydrolyzing site. They showed that only subsites -1 and -2 at the nonreducing end of TVAI are effective in the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkages, leading to weak interactions between substrates and the enzyme. Domain N of TVAI is a starch-binding domain acting as an anchor in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme. In this study, additional substrates were also found to bind to domain N, suggesting that domain N also functions as a pullulan-binding domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Medicine, Kagawa University, Japan.