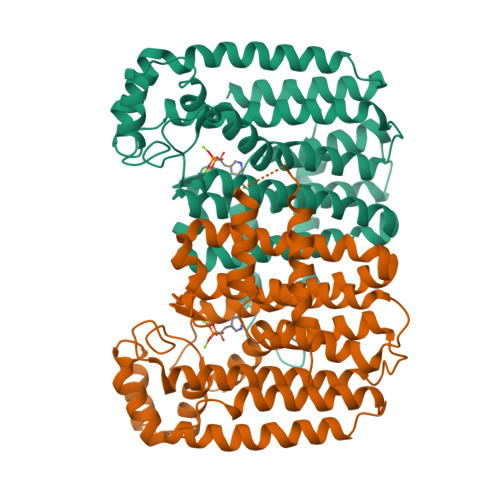
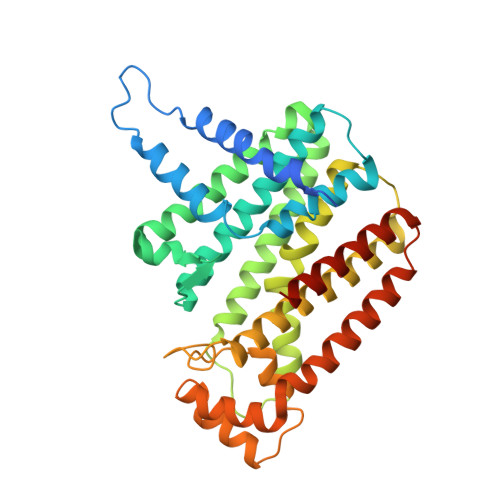
Targeting a uniquely nonspecific prenyl synthase with bisphosphonates to combat cryptosporidiosis
Artz, J.D., Dunford, J.E., Arrowood, M.J., Dong, A., Chruszcz, M., Kavanagh, K.L., Minor, W., Russell, R.G., Ebetino, F.H., Oppermann, U., Hui, R.(2008) Chem Biol 15: 1296-1306
- PubMed: 19101474
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2O1O, 2Q58 - PubMed Abstract:
Cryptosporidiosis is a neglected disease without a wholly effective drug. We present a study demonstrating nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (N-BPs) to be capable of inhibiting Cryptosporidium parvum at low micromolar concentrations in infected MDCK cells. Predictably, the mechanism of action is based on inhibition of biosynthesis of isoprenoids but the target enzyme is unexpectedly a distinctive C. parvum enzyme dubbed nonspecific polyprenyl pyrophosphate synthase (CpNPPPS). This enzyme produces various isoprenoid products larger than FPP and is inhibited by N-BPs at subnanomolar concentrations. It is part of an isoprenoid pathway in Cryptosporidium distinctly different from other organisms. The proposed mechanism of action is corroborated by crystal structures of the enzyme with risedronate and zoledronate bound showing how this enzyme's unique chain length determinant region enables it to accommodate larger substrates and products. These results, combined with existing data on their clinical use, demonstrate that N-BPs are very promising anticryptosporidial drug candidates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, University of Toronto, 101 College Street, Toronto, ON M5G 1L7, Canada.