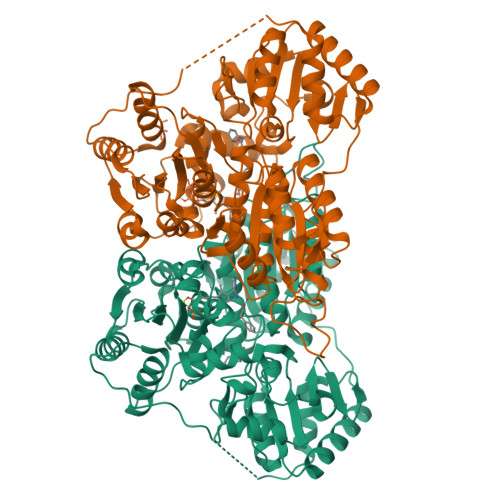
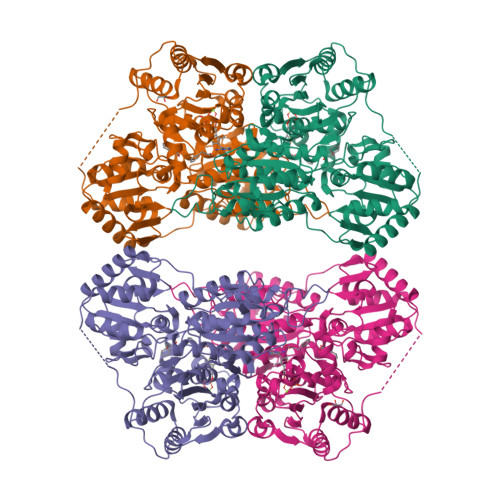
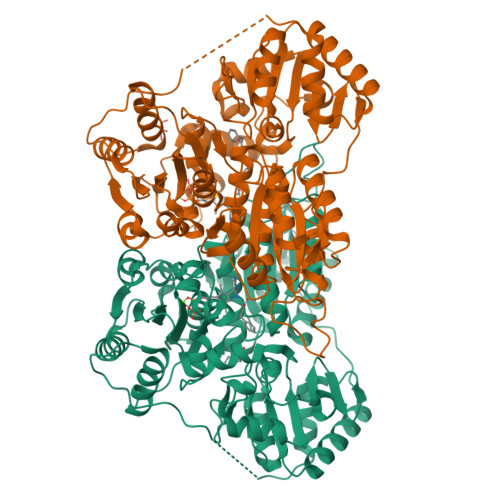
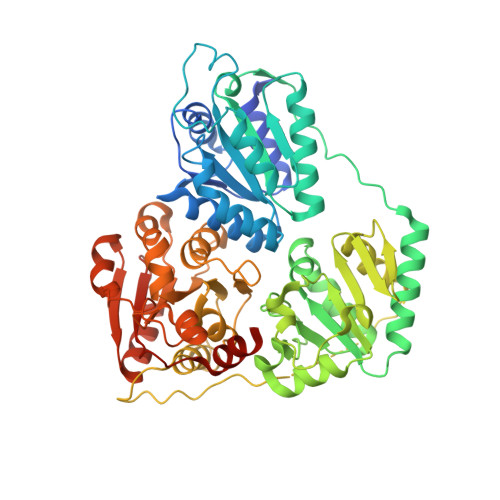
Molecular mechanism of allosteric substrate activation in a thiamine diphosphate-dependent decarboxylase.
Versees, W., Spaepen, S., Wood, M.D., Leeper, F.J., Vanderleyden, J., Steyaert, J.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 35269-35278
- PubMed: 17905741
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706048200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Q5J, 2Q5L, 2Q5O, 2Q5Q - PubMed Abstract:
Thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzymes are involved in a wide variety of metabolic pathways. The molecular mechanism behind active site communication and substrate activation, observed in some of these enzymes, has since long been an area of debate. Here, we report the crystal structures of a phenylpyruvate decarboxylase in complex with its substrates and a covalent reaction intermediate analogue. These structures reveal the regulatory site and unveil the mechanism of allosteric substrate activation. This signal transduction relies on quaternary structure reorganizations, domain rotations, and a pathway of local conformational changes that are relayed from the regulatory site to the active site. The current findings thus uncover the molecular mechanism by which the binding of a substrate in the regulatory site is linked to the mounting of the catalytic machinery in the active site in this thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Ultrastructure, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussels, Belgium. wversees@vub.ac.be