Glutathione Reductase and Thioredoxin Reductase at the Crossroad: The Structure of Schistosoma Mansoni Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase
Angelucci, F., Miele, A.E., Boumis, G., Dimastrogiovanni, D., Brunori, M., Bellelli, A.(2008) Proteins 72: 936
- PubMed: 18300227
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21986
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V6O - PubMed Abstract:
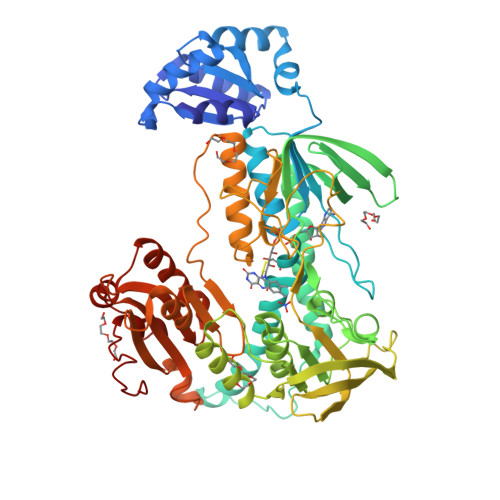
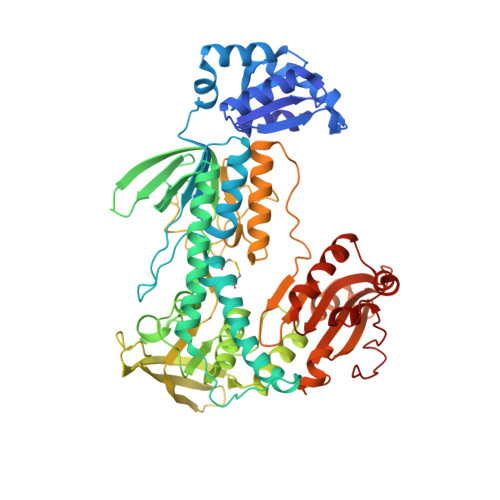
Thioredoxin glutathione reductase (TGR) is a key flavoenzyme expressed by schistosomes that bridges two detoxification pathways crucial for the parasite survival in the host's organism. In this article we report the crystal structure (at 2.2 A resolution) of TGR from Schistosoma mansoni (SmTGR), deleted in the last two residues. The structure reveals the peculiar architecture of this chimeric enzyme: the small Glutaredoxin (Grx) domain at the N-terminus is joined to the large thioredoxin reductase (TR) one via an extended complementary surface, involving residues not conserved in the Grx superfamily; the TR domain interacts with an identical partner via its C-terminal domain, forming a dimer with a twisted "W" shape. Although lacking the penultimate Selenocysteine residue (Sec), the enzyme is still able to reduce oxidized glutathione. These data update the interpretation of the interdomain communication in TGR enzymes. The possible function of this enzyme in pathogenic parasites is discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemical Sciences A Rossi Fanelli, Istituto Pasteur Fondazione Cenci-Bolognetti and CNR Institute of Molecular Biology and Pathology, Sapienza University of Rome, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, 00185 Rome, Italy.