Modification of porous protein crystals in development of biohybrid materials
Koshiyama, T., Kawaba, N., Hikage, T., Shirai, M., Miura, Y., Huang, C.-Y., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, Y., Ueno, T.(2010) Bioconjug Chem 21: 264-269
- PubMed: 20099839
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bc9003052
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3A2G - PubMed Abstract:
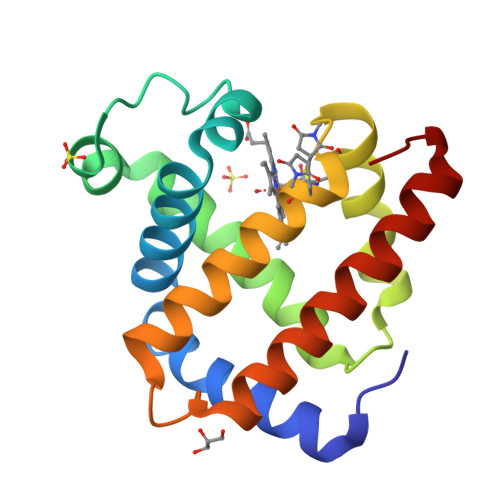
Protein assemblies have attracted increasing attention for construction of biohybrid materials. Protein crystals can also be regarded as solid protein assemblies. The present work demonstrates that protein crystals can be employed as porous biomaterials by site-specific modifications of the crystals of recombinant sperm whale myoglobin mutants. The myoglobin crystals of space group P6 provide hexagonal pores consisting of the building blocks of six Mb molecules, which form a pore with a diameter of 40 A. On the basis of the lattice structure of the Mb crystals, we have selected appropriate residues located on the surface of the pores for replacement with cysteine. This enables modification of the pore surface via coupling with maleimide derivatives. We have succeeded in crystallizing the modified Mb mutants, retaining the P6 lattice, and consistently aligning nanosized functional molecules such as fluorescein, eosin, and Ru(bpy)(3) into the hexagonal pores of the Mb crystals. Our strategy for site-specific modification of protein crystal pores is applicable to various protein crystals with porous structures. We believe that modified porous protein crystals will provide attractive candidates for novel solid materials in nanotechnology applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences, Funai Center, Kyoto University Katsura, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan.