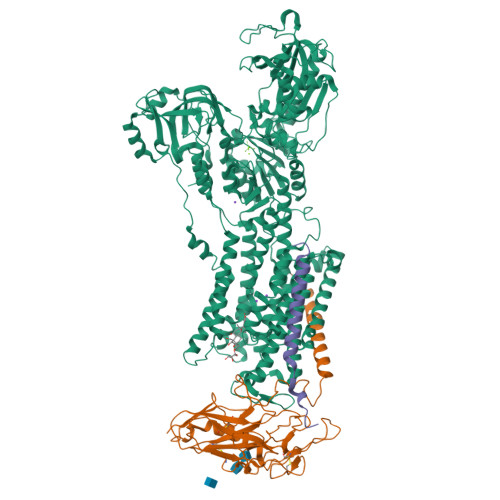
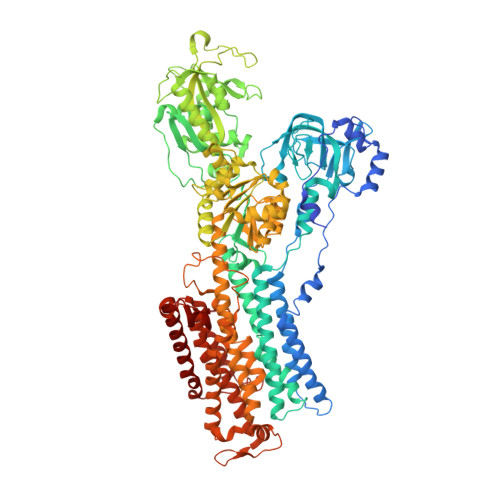
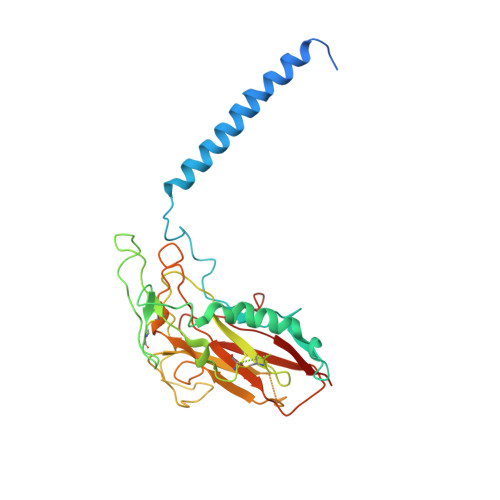
Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase) with bound potassium and ouabain.
Ogawa, H., Shinoda, T., Cornelius, F., Toyoshima, C.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 13742-13747
- PubMed: 19666591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907054106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3A3Y - PubMed Abstract:
The sodium-potassium pump (Na(+),K(+)-ATPase) is responsible for establishing Na(+) and K(+) concentration gradients across the plasma membrane and therefore plays an essential role in, for instance, generating action potentials. Cardiac glycosides, prescribed for congestive heart failure for more than 2 centuries, are efficient inhibitors of this ATPase. Here we describe a crystal structure of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase with bound ouabain, a representative cardiac glycoside, at 2.8 A resolution in a state analogous to E2.2K(+).Pi. Ouabain is deeply inserted into the transmembrane domain with the lactone ring very close to the bound K(+), in marked contrast to previous models. Due to antagonism between ouabain and K(+), the structure represents a low-affinity ouabain-bound state. Yet, most of the mutagenesis data obtained with the high-affinity state are readily explained by the present crystal structure, indicating that the binding site for ouabain is essentially the same. According to a homology model for the high affinity state, it is a closure of the binding cavity that confers a high affinity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032, Japan.