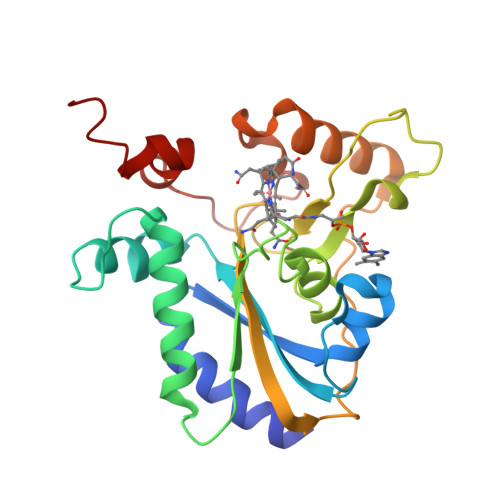
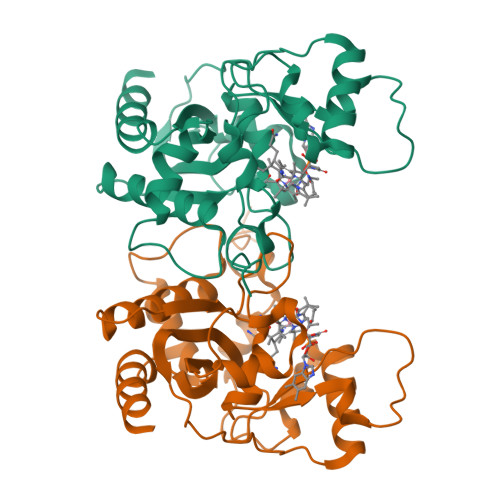
Structural basis of multifunctionality in a vitamin B12-processing enzyme.
Koutmos, M., Gherasim, C., Smith, J.L., Banerjee, R.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 29780-29787
- PubMed: 21697092
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.261370
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SBY, 3SBZ, 3SC0 - PubMed Abstract:
An early step in the intracellular processing of vitamin B(12) involves CblC, which exhibits dual reactivity, catalyzing the reductive decyanation of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B(12)), and the dealkylation of alkylcobalamins (e.g. methylcobalamin; MeCbl). Insights into how the CblC scaffold supports this chemical dichotomy have been unavailable despite it being the most common locus of patient mutations associated with inherited cobalamin disorders that manifest in both severe homocystinuria and methylmalonic aciduria. Herein, we report structures of human CblC, with and without bound MeCbl, which provide novel biochemical insights into its mechanism of action. Our results reveal that CblC is the most divergent member of the NADPH-dependent flavin reductase family and can use FMN or FAD as a prosthetic group to catalyze reductive decyanation. Furthermore, CblC is the first example of an enzyme with glutathione transferase activity that has a sequence and structure unrelated to the GST superfamily. CblC thus represents an example of evolutionary adaptation of a common structural platform to perform diverse chemistries. The CblC structure allows us to rationalize the biochemical basis of a number of pathological mutations associated with severe clinical phenotypes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry and the Life Sciences Institute, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-0600, USA.