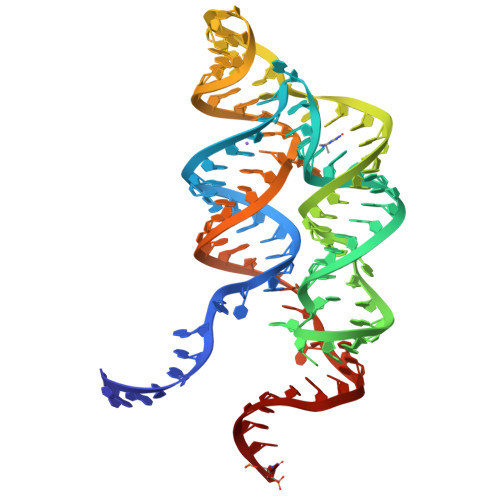
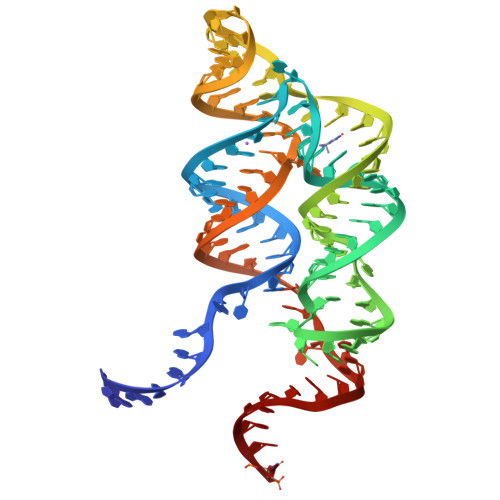
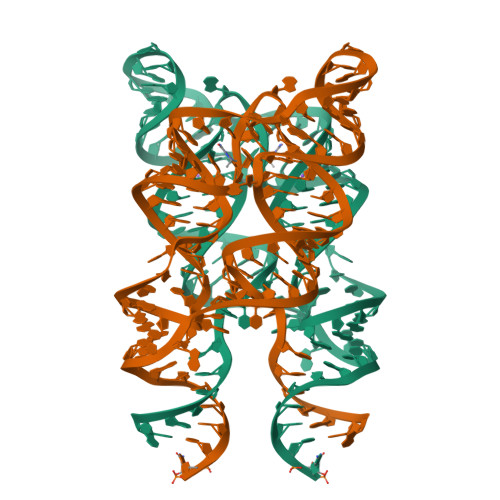
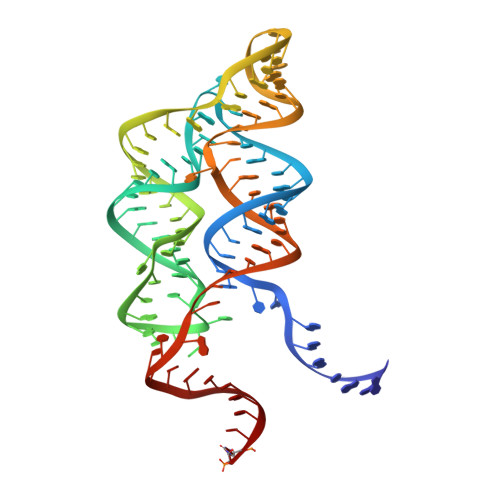
Long-range pseudoknot interactions dictate the regulatory response in the tetrahydrofolate riboswitch.
Huang, L., Ishibe-Murakami, S., Patel, D.J., Serganov, A.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 14801-14806
- PubMed: 21873197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111701108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SUH, 3SUX, 3SUY - PubMed Abstract:
Tetrahydrofolate (THF), a biologically active form of the vitamin folate (B(9)), is an essential cofactor in one-carbon transfer reactions. In bacteria, expression of folate-related genes is controlled by feedback modulation in response to specific binding of THF and related compounds to a riboswitch. Here, we present the X-ray structures of the THF-sensing domain from the Eubacterium siraeum riboswitch in the ligand-bound and unbound states. The structure reveals an "inverted" three-way junctional architecture, most unusual for riboswitches, with the junction located far from the regulatory helix P1 and not directly participating in helix P1 formation. Instead, the three-way junction, stabilized by binding to the ligand, aligns the riboswitch stems for long-range tertiary pseudoknot interactions that contribute to the organization of helix P1 and therefore stipulate the regulatory response of the riboswitch. The pterin moiety of the ligand docks in a semiopen pocket adjacent to the junction, where it forms specific hydrogen bonds with two moderately conserved pyrimidines. The aminobenzoate moiety stacks on a guanine base, whereas the glutamate moiety does not appear to make strong interactions with the RNA. In contrast to other riboswitches, these findings demonstrate that the THF riboswitch uses a limited number of available determinants for ligand recognition. Given that modern antibiotics target folate metabolism, the THF riboswitch structure provides insights on mechanistic aspects of riboswitch function and may help in manipulating THF levels in pathogenic bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065, USA. huanglilisioc@hotmail.com