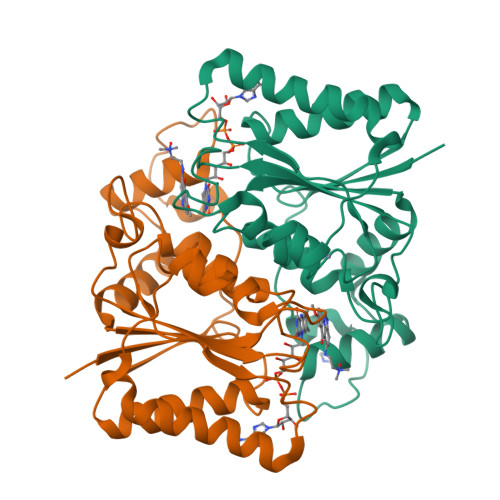
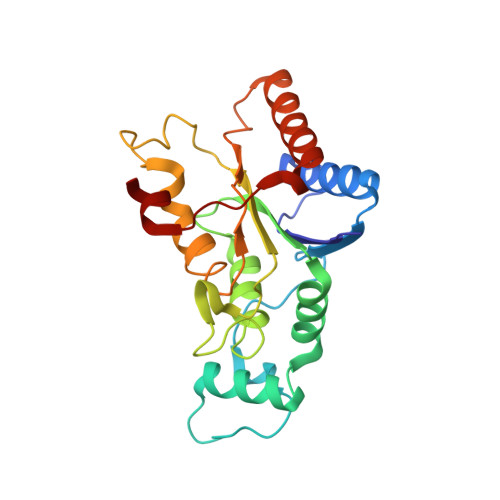
Novel Inhibitors of NRH:Quinone Oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2): Crystal Structures, Biochemical Activity, and Intracellular Effects of Imidazoacridin-6-ones.
Dunstan, M.S., Barnes, J., Humphries, M., Whitehead, R.C., Bryce, R.A., Leys, D., Stratford, I.J., Nolan, K.A.(2011) J Med Chem 54: 6597-6611
- PubMed: 21859103
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm200416e
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TE7, 3TEM - PubMed Abstract:
Imidazoacridin-6-ones are shown to be potent nanomolar inhibitors of the enzyme NQO2. By use of computational molecular modeling, a reliable QSAR was established, relating inhibitory potency with calculated binding affinity. Further, crystal structures of NQO2 containing two of the imidazoacridin-6-ones have been solved. To generate compounds with reduced off-target (DNA binding) effects, an N-oxide moiety was introduced into the tertiary aminoalkyl side chain of the imidazoacridin-6-ones. This resulted in substantially less toxicity in a panel of eight cancer cell lines, decreased protein binding, and reduced DNA binding and nuclear accumulation. Finally, one of the N-oxides showed potent ability to inhibit the enzymatic function of NQO2 in cells, and therefore, it may be useful as a pharmacological probe to study the properties of the enzyme in vitro and in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, University of Manchester and Manchester Cancer Research Centre, Manchester M13 9PT, U.K.