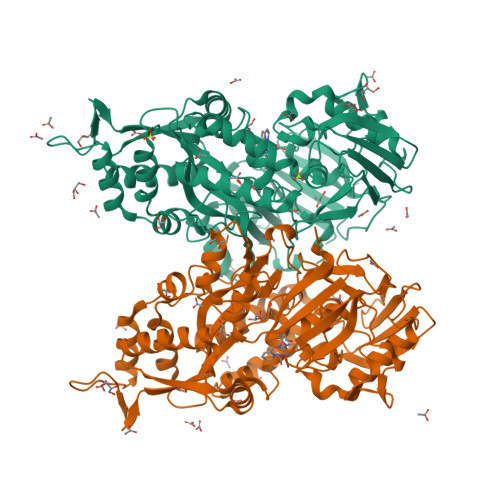
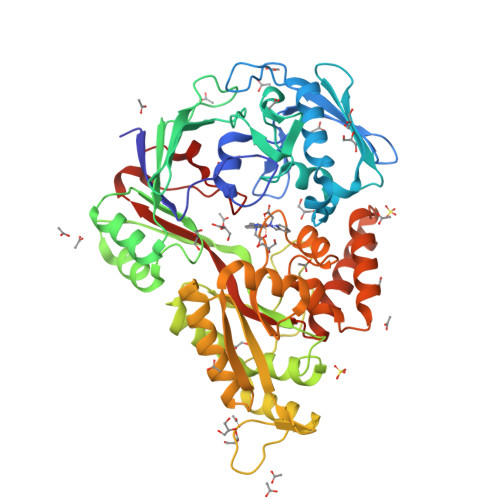
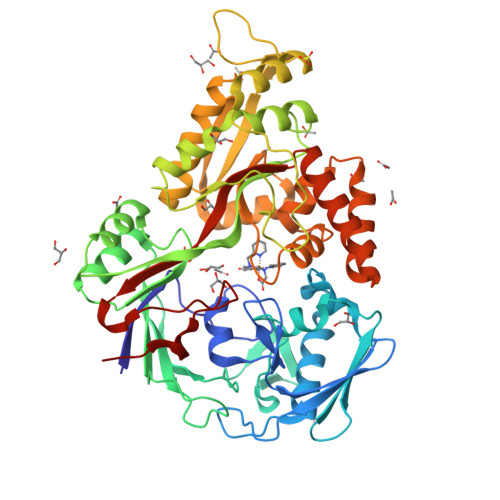
The structure of the periplasmic nickel-binding protein NikA provides insights for artificial metalloenzyme design.
Cherrier, M.V., Girgenti, E., Amara, P., Iannello, M., Marchi-Delapierre, C., Fontecilla-Camps, J.C., Menage, S., Cavazza, C.(2012) J Biol Inorg Chem 17: 817-829
- PubMed: 22526565
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-012-0899-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DCX, 4DCY - PubMed Abstract:
Understanding the interaction of a protein with a relevant ligand is crucial for the design of an artificial metalloenzyme. Our own interest is focused on the synthesis of artificial monooxygenases. In an initial effort, we have used the periplasmic nickel-binding protein NikA from Escherichia coli and iron complexes in which N(2)Py(2) ligands (where Py is pyridine) have been varied in terms of charge, aromaticity, and size. Six "NikA/iron complex" hybrids have been characterized by X-ray crystallography, and their interactions and solution properties have been studied. The hybrids are stable as indicated by their K (d) values, which are all in the micromolar range. The X-ray structures show that the ligands interact with NikA through salt bridges with arginine residues and π-stacking with a tryptophan residue. We have further characterized these interactions using quantum mechanical calculations and determined that weak CH/π hydrogen bonds finely modulate the stability differences between hybrids. We emphasize the important role of the tryptophan residues. Thus, our study aims at the complete characterization of the factors that condition the interaction of an artificial ligand and a protein and their implications for catalysis. Besides its potential usefulness in the synthesis of artificial monooxygenases, our approach should be generally applicable in the field of artificial metalloenzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Biologie Structurale Jean-Pierre Ebel, Groupe Métalloproteines, UMR 5075, CEA, CNRS, Université Joseph Fourier Grenoble 1, 41 rue Horowitz, 38027, Grenoble Cedex 1, France.