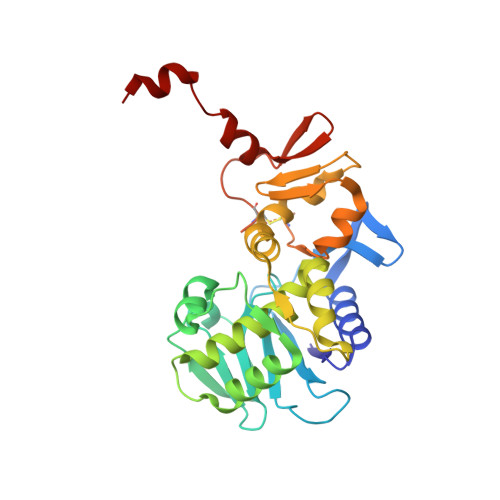
The crystal structure of shiga toxin type 2 with bound disaccharide guides the design of a heterobifunctional toxin inhibitor.
Jacobson, J.M., Yin, J., Kitov, P.I., Mulvey, G., Griener, T.P., James, M.N., Armstrong, G., Bundle, D.R.(2014) J Biol Chem 289: 885-894
- PubMed: 24225957
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.518886
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M1U - PubMed Abstract:
Shiga toxin type 2 (Stx2a) is clinically most closely associated with enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7-mediated hemorrhagic colitis that sometimes progresses to hemolytic-uremic syndrome. The ability to express the toxin has been acquired by other Escherichia coli strains, and outbreaks of food poisoning have caused significant mortality rates as, for example, in the 2011 outbreak in northern Germany. Stx2a, an AB5 toxin, gains entry into human cells via the glycosphingolipid receptor Gb3. We have determined the first crystal structure of a disaccharide analog of Gb3 bound to the B5 pentamer of Stx2a holotoxin. In this Gb3 analog,-GalNAc replaces the terminal-Gal residue. This co-crystal structure confirms previous inferences that two of the primary binding sites identified in theB5 pentamer of Stx1 are also functional in Stx2a. This knowledge provides a rationale for the synthesis and evaluation of heterobifunctional antagonists for E. coli toxins that target Stx2a. Incorporation of GalNAc Gb3 trisaccharide in a heterobifunctional ligand with an attached pyruvate acetal, a ligand for human amyloid P component, and conjugation to poly[acrylamide-co-(3-azidopropylmethacrylamide)] produced a polymer that neutralized Stx2a in a mouse model of Shigatoxemia.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Chemistry, Alberta Glycomics Centre, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2G2, Canada.