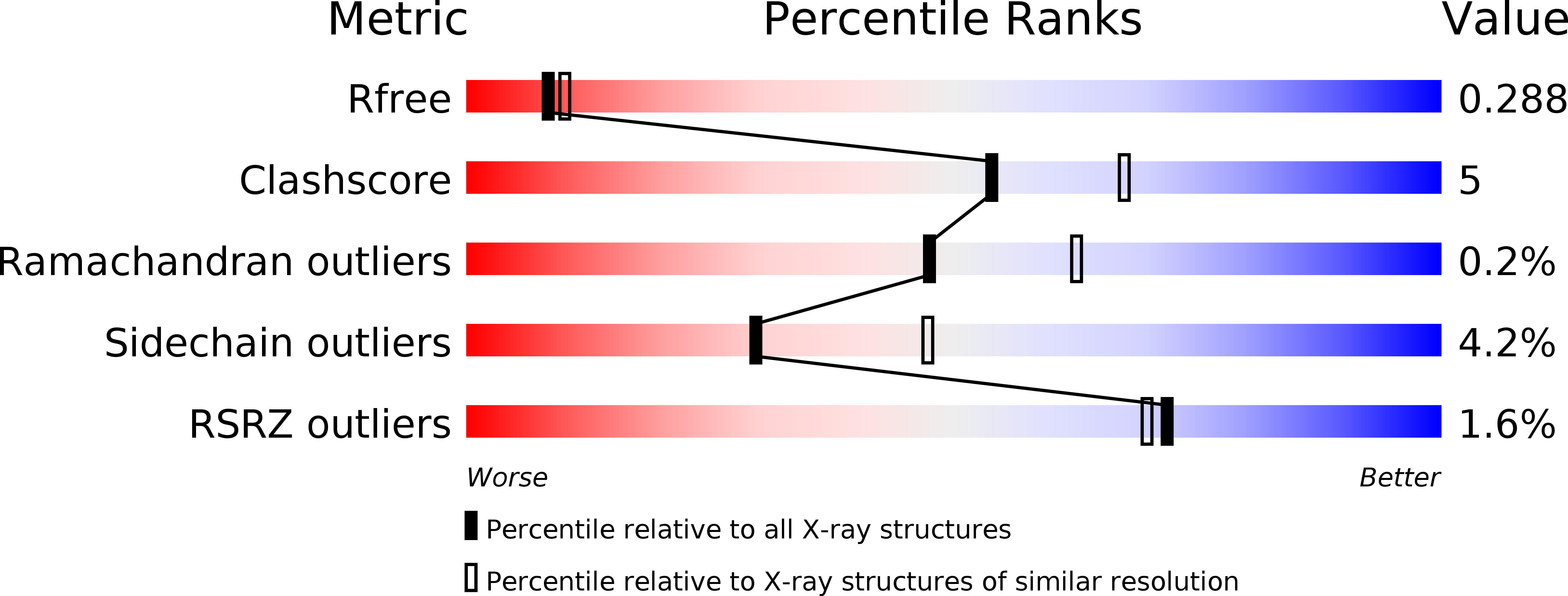
X-ray crystal structures of Enterococcus faecalis thymidylate synthase with folate binding site inhibitors.
Catalano, A., Luciani, R., Carocci, A., Cortesi, D., Pozzi, C., Borsari, C., Ferrari, S., Mangani, S.(2016) Eur J Med Chem 123: 649-664
- PubMed: 27517810
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.07.066
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4O7U, 5J7W - PubMed Abstract:
Infections caused by Enterococcus faecalis (Ef) represent nowadays a relevant health problem. We selected Thymidylate synthase (TS) from this organism as a potential specific target for antibacterial therapy. We have previously demonstrated that species-specific inhibition of the protein can be achieved despite the relatively high structural similarity among bacterial TSs and human TS. We had previously obtained the EfTS crystal structure of the protein in complex with the metabolite 5-formyl-tetrahydrofolate (5-FTHF) suggesting the protein role as metabolite reservoir; however, protein-inhibitors complexes were still missing. In the present work we identified some inhibitors bearing the phthalimidic core from our in-house library and we performed crystallographic screening towards EfTS. We obtained two X-ray crystallographic structures: the first with a weak phthalimidic inhibitor bound in one subunit and 5-hydroxymethylene-6-hydrofolic acid (5-HMHF) in the other subunit; a second X-ray structure complex with methotrexate. The structural information achieved confirm the role of EfTS as an enzyme involved in the folate pool system and provide a structural basis for structure-based drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Dipartimento di Farmacia-Scienze del Farmaco, Università degli Studi di Bari "Aldo Moro", Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy.