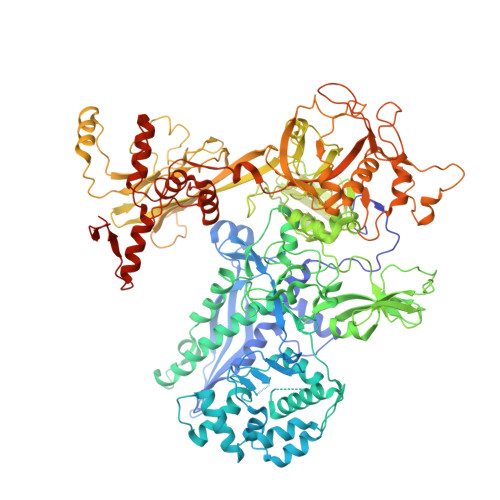
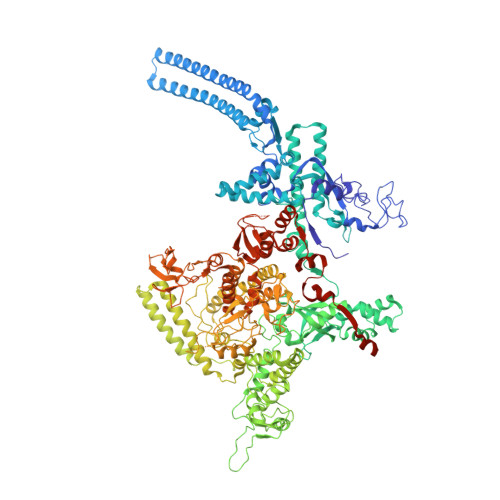
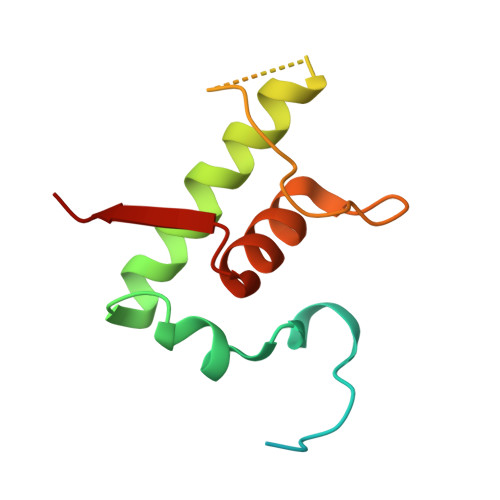
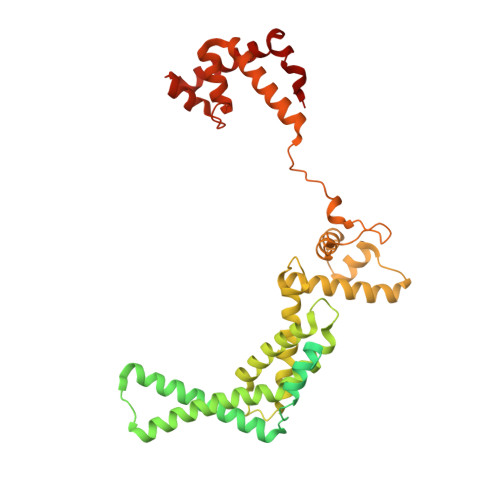
Rifamycin congeners kanglemycins are active against rifampicin-resistant bacteria via a distinct mechanism.
Peek, J., Lilic, M., Montiel, D., Milshteyn, A., Woodworth, I., Biggins, J.B., Ternei, M.A., Calle, P.Y., Danziger, M., Warrier, T., Saito, K., Braffman, N., Fay, A., Glickman, M.S., Darst, S.A., Campbell, E.A., Brady, S.F.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 4147-4147
- PubMed: 30297823
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06587-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CCE, 6CCV, 6DCF - PubMed Abstract:
Rifamycin antibiotics (Rifs) target bacterial RNA polymerases (RNAPs) and are widely used to treat infections including tuberculosis. The utility of these compounds is threatened by the increasing incidence of resistance (Rif R ). As resistance mechanisms found in clinical settings may also occur in natural environments, here we postulated that bacteria could have evolved to produce rifamycin congeners active against clinically relevant resistance phenotypes. We survey soil metagenomes and identify a tailoring enzyme-rich family of gene clusters encoding biosynthesis of rifamycin congeners (kanglemycins, Kangs) with potent in vivo and in vitro activity against the most common clinically relevant Rif R mutations. Our structural and mechanistic analyses reveal the basis for Kang inhibition of Rif R RNAP. Unlike Rifs, Kangs function through a mechanism that includes interfering with 5'-initiating substrate binding. Our results suggest that examining soil microbiomes for new analogues of clinically used antibiotics may uncover metabolites capable of circumventing clinically important resistance mechanisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Genetically Encoded Small Molecules, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY, 10065, USA.