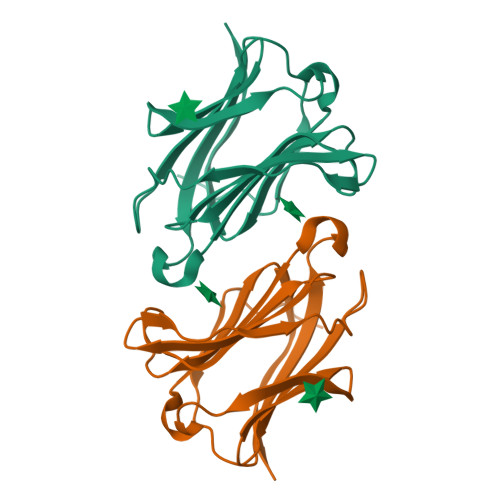
Structures of human galectin-10/monosaccharide complexes demonstrate potential of monosaccharides as effectors in forming Charcot-Leyden crystals.
Itoh, A., Nonaka, Y., Nakakita, S.I., Yoshida, H., Nishi, N., Nakamura, T., Kamitori, S.(2020) Biochem Biophys Res Commun
- PubMed: 32081418
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.037
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6L64, 6L67, 6L68, 6L6A, 6L6B, 6L6C, 6L6D - PubMed Abstract:
The galectins are a family of β-galactoside-specific animal lectins, and have attracted much attention as novel regulators of the immune system. Galectin-10 is well-expressed in eosinophils, and spontaneously forms Charcot-Leyden crystals (CLCs), during prolonged eosinophilic inflammatory reactions, which are frequently observed in eosinophilic diseases. Although biochemical and structural characterizations of galectin-10 have been done, its biological role and molecular mechanism are still unclear, and few X-ray structures of galectin-10 in complex with monosaccharides/oligosaccharides have been reported. Here, X-ray structures of galectin-10 in complexes with seven monosaccharides are presented with biochemical analyses to detect interactions of galectin-10 with monosaccharides/oligosaccharides. Galectin-10 forms a homo-dimer in the face-to-face orientation, and the monosaccharides bind to the carbohydrate recognition site composed of amino acid residues from two galectin-10 molecules of dimers, suggesting that galectin-10 dimer likely captures the monosaccharides in solution and in vivo. d-Glucose, d-allose, d-arabinose, and D-N-acetylgalactosamine bind to the interfaces between galectin-10 dimers in crystals, and they affect the stability of molecular packing in crystals, leading to easy-dissolving of CLCs, and/or inhibiting the formation of CLCs. These monosaccharides may serve as effectors of G10 to form CLCs in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Life Science Research Center and Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Miki-cho, Kagawa, Japan.