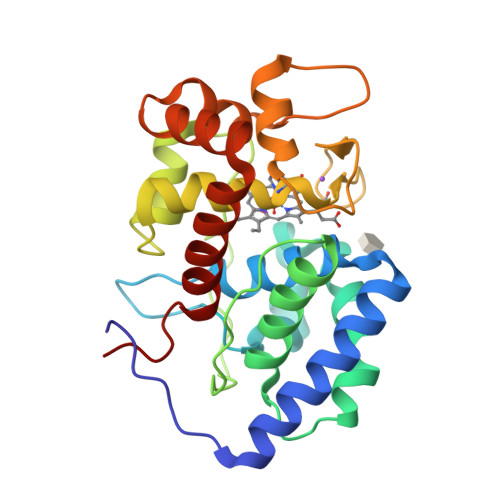
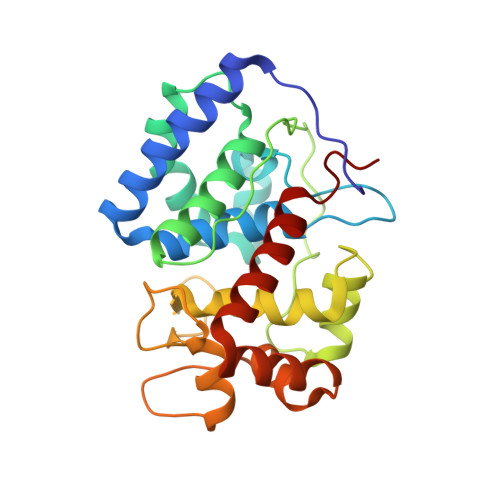
A sorghum ascorbate peroxidase with four binding sites has activity against ascorbate and phenylpropanoids.
Zhang, B., Lewis, J.A., Vermerris, W., Sattler, S.E., Kang, C.(2023) Plant Physiol 192: 102-118
- PubMed: 36575825
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiac604
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DJR, 8DJS, 8DJT, 8DJU, 8DJW, 8DJX - PubMed Abstract:
In planta, H2O2 is produced as a by-product of enzymatic reactions and during defense responses. Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) is a key enzyme involved in scavenging cytotoxic H2O2. Here, we report the crystal structure of cytosolic APX from sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) (Sobic.001G410200). While the overall structure of SbAPX was similar to that of other APXs, SbAPX uniquely displayed four bound ascorbates rather than one. In addition to the ɣ-heme pocket identified in other APXs, ascorbates were bound at the δ-meso and two solvent-exposed pockets. Consistent with the presence of multiple binding sites, our results indicated that the H2O2-dependent oxidation of ascorbate displayed positive cooperativity. Bound ascorbate at two surface sites established an intricate proton network with ascorbate at the ɣ-heme edge and δ-meso sites. Based on crystal structures, steady-state kinetics, and site-directed mutagenesis results, both ascorbate molecules at the ɣ-heme edge and the one at the surface are expected to participate in the oxidation reaction. We provide evidence that the H2O2-dependent oxidation of ascorbate by APX produces a C2-hydrated bicyclic hemiketal form of dehydroascorbic acid at the ɣ-heme edge, indicating two successive electron transfers from a single-bound ascorbate. In addition, the δ-meso site was shared with several organic compounds, including p-coumaric acid and other phenylpropanoids, for the potential radicalization reaction. Site-directed mutagenesis of the critical residue at the ɣ-heme edge (R172A) only partially reduced polymerization activity. Thus, APX removes stress-generated H2O2 with ascorbates, and also uses this same H2O2 to potentially fortify cell walls via oxidative polymerization of phenylpropanoids in response to stress.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington 99164, USA.