Rational Design of Macrocyclic Noncovalent Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 M pro from a DNA-Encoded Chemical Library Screening Hit That Demonstrate Potent Inhibition against Pan-Coronavirus Homologues and Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Variants.
Wang, X., Gotchev, D., Fan, K.Y., Vega, M.M., Mani, N., McGovern-Gooch, K., Cuconati, A., Tercero, B., Wang, X., Carpino, P., Maskos, K., Centrella, P.A., Schmitt, A., Preuss, F., Prasad, A., Chen, C.Y., Clark, M.A., Guilinger, J.P., Johnstone, S., von Konig, K., Keefe, A.D., Liu, J., Turcotte, S., Zhang, Y., Konz Makino, D.L., Lam, A.M., Cole, A.G., Sofia, M.J.(2024) J Med Chem 67: 19623-19667
- PubMed: 39453309
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
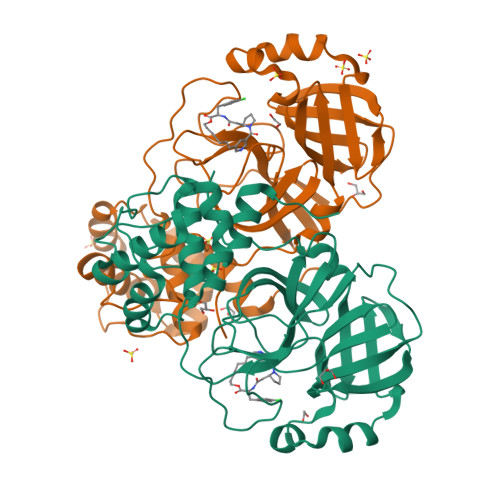
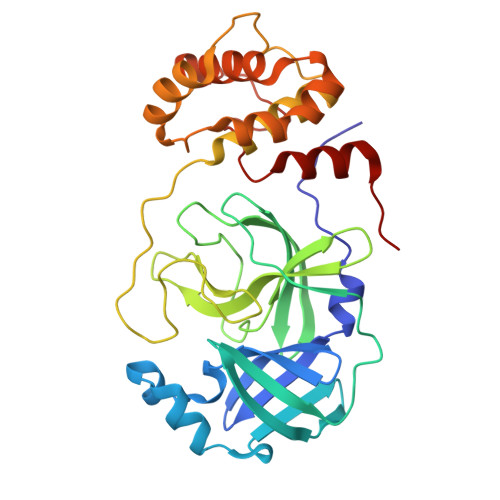
9GIJ, 9GIL - PubMed Abstract:
The recent global COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted treatments for coronavirus infection as an unmet medical need. The main protease (M pro ) has been an important target for the development of SARS-CoV-2 direct-acting antivirals. Nirmatrelvir as a covalent M pro inhibitor was the first such approved therapy. Although M pro inhibitors of various chemical classes have been reported, they are generally less active against nirmatrelvir-resistant variants and have limited pan-coronavirus potential, presenting a significant human health risk upon future outbreaks. We here present a novel approach and utilized DNA-encoded chemical library screening to identify the noncovalent M pro inhibitor 5 , which demonstrated a distinct binding mode to nirmatrelvir. A macrocyclization strategy designed to lock the active conformation resulted in lactone 12 with significantly improved antiviral activity. Further optimization led to the potent lactam 26 , which demonstrated exceptional potency against nirmatrelvir-resistant variants as well as against a panel of viral main proteases from other coronaviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Arbutus Biopharma Inc., 701 Veterans Circle, Warminster, Pennsylvania 18974, United States.