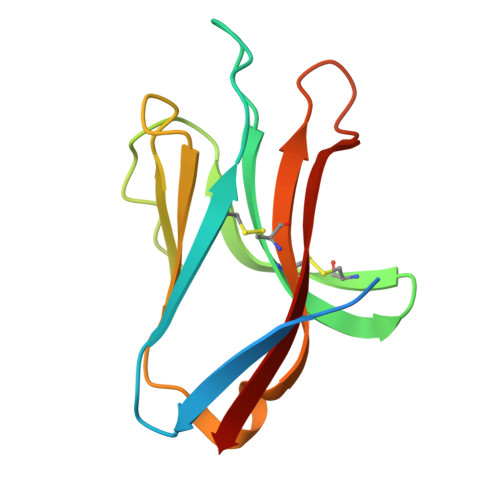
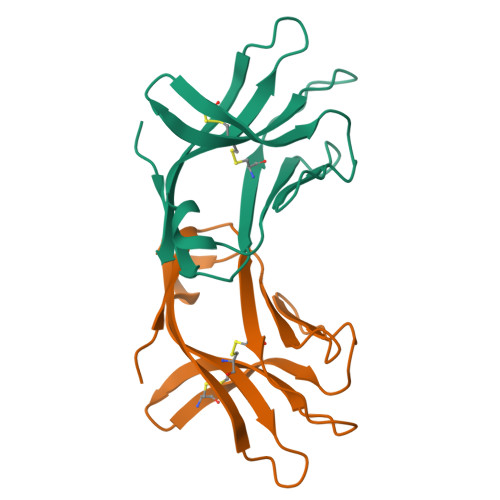
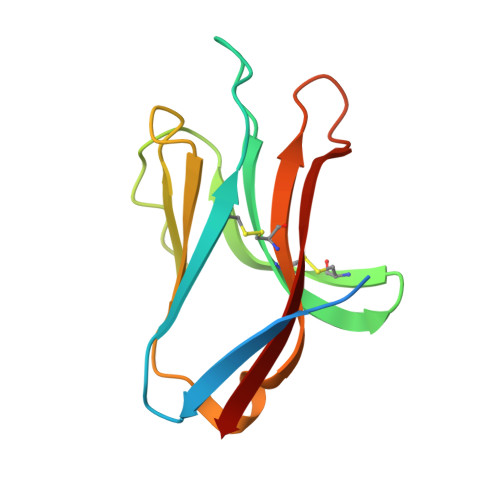
The Three-Dimensional Structure of the Human Nk Cell Receptor Nkp44, a Triggering Partner in Natural Cytotoxicity
Cantoni, C., Ponassi, M., Biassoni, R., Conte, R., Spallarossa, A., Moretta, A., Moretta, L., Bolognesi, M., Bordo, D.(2003) Structure 11: 725
- PubMed: 12791260
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00095-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HKF - PubMed Abstract:
Natural killer (NK) cells direct cytotoxicity against tumor or virally infected cells. NK cell activation depends on a fine balance between inhibitory and activating receptors. NKp44 is a cytotoxicity activating receptor composed of one Ig-like extracellular domain, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic domain. The 2.2 A crystal structure shows that the NKp44 Ig domain forms a saddle-shaped dimer, where a charged surface groove protrudes from the core structure in each subunit. NKp44 Ig domain disulfide bridge topology defines a new Ig structural subfamily. The data presented are a first step toward understanding the molecular basis for ligand recognition by natural cytotoxicity receptors, whose key role in the immune system is established, but whose cellular ligands are still elusive.
Organizational Affiliation:
Dipartimento di Medicina Sperimentale, Università di Genova, Via L.B. Alberti 1, 16132 Genova, Italy.