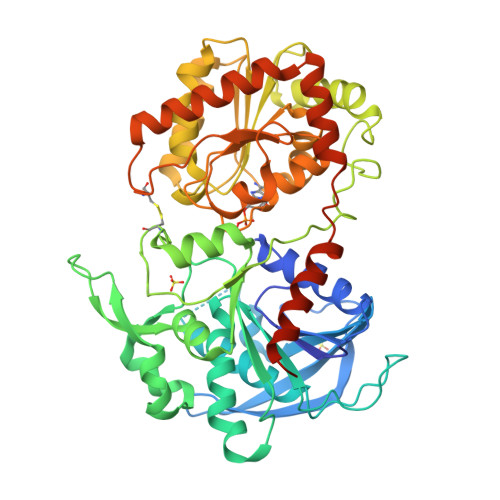
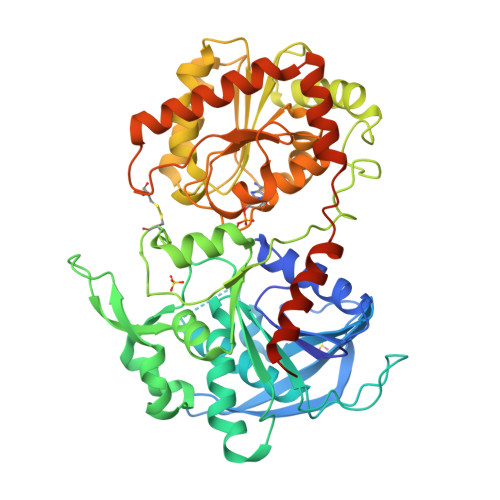
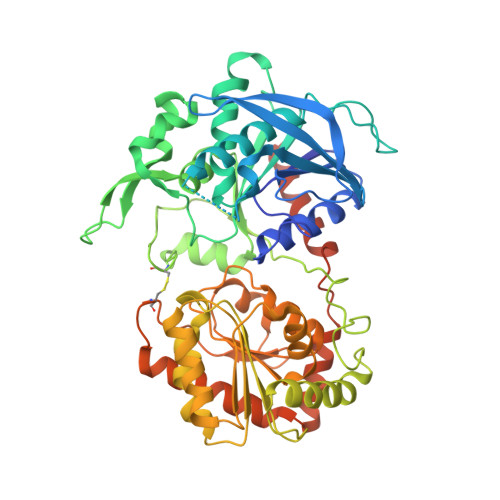
Interdomain Disulfide Bridge in the Rice Granule Bound Starch Synthase I Catalytic Domain as Elucidated by X-Ray Structure Analysis
Momma, M., Fujimoto, Z.(2012) Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76: 1591-1595
- PubMed: 22878205
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120305
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VUE, 3VUF - PubMed Abstract:
The catalytic domain of rice (Oryza sativa japonica) granule bound starch synthase I (OsGBSSI-CD) was overexpressed and the three-dimensional structures of the ligand-free and ADP-bound forms were determined. The structures were similar to those reported for bacterial and archaeal glycogen synthases, which belong to glycosyltransferase family 5. They had Rossmann fold N- and C-domains connected by canonical two-hinge peptides, and an interdomain disulfide bond that appears to be conserved in the Poaceae plant family. The presence of three covalent linkages might explain why both OsGBSSI-CD structures adopted only the closed domain arrangement.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomolecular Research Unit, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, 2-1-2 Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8602, Japan. momma@affrc.go.jp