Cwp84, a Clostridium Difficile Cysteine Protease, Exhibits Conformational Flexibility in the Absence of its Propeptide
Bradshaw, W.J., Roberts, A.K., Shone, C.C., Acharya, K.R.(2015) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 71: 295
- PubMed: 25760704
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X15001065
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4D59, 4D5A - PubMed Abstract:
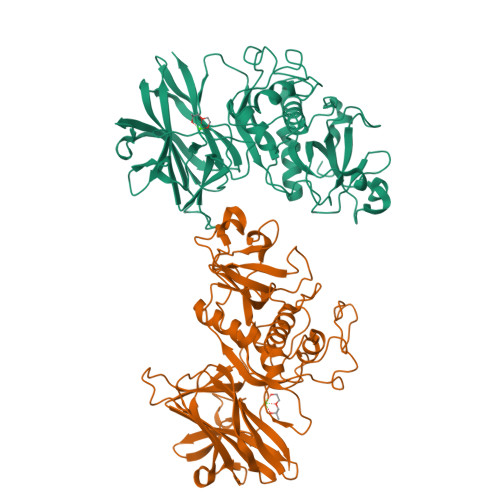
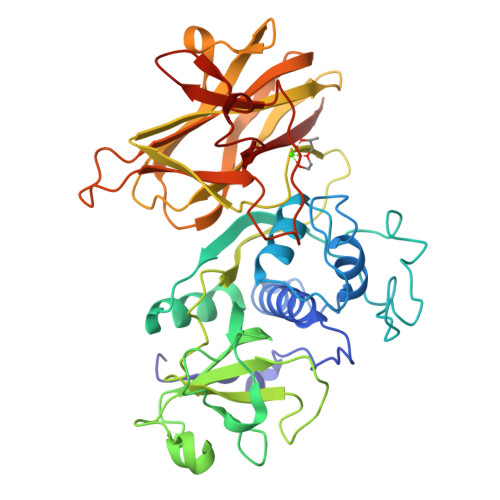
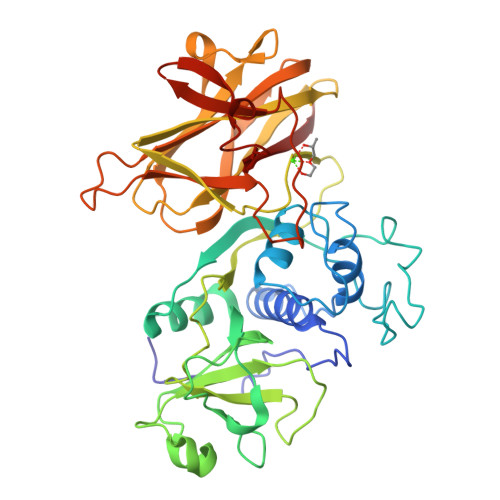
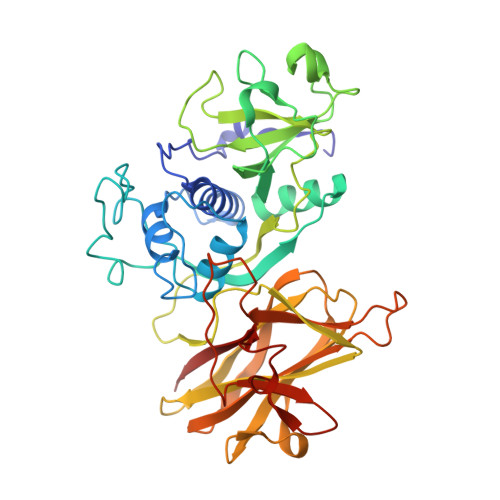
In recent decades, the global healthcare problems caused by Clostridium difficile have increased at an alarming rate. A greater understanding of this antibiotic-resistant bacterium, particularly with respect to how it interacts with the host, is required for the development of novel strategies for fighting C. difficile infections. The surface layer (S-layer) of C. difficile is likely to be of significant importance to host-pathogen interactions. The mature S-layer is formed by a proteinaceous array consisting of multiple copies of a high-molecular-weight and a low-molecular-weight S-layer protein. These components result from the cleavage of SlpA by Cwp84, a cysteine protease. The structure of a truncated Cwp84 active-site mutant has recently been reported and the key features have been identified, providing the first structural insights into the role of Cwp84 in the formation of the S-layer. Here, two structures of Cwp84 after propeptide cleavage are presented and the three conformational changes that are observed are discussed. These changes result in a reconfiguration of the active site and exposure of the hydrophobic pocket.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology and Biochemistry, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath BA2 7AY, England.