Characterization of novel lectins from Burkholderia pseudomallei and Chromobacterium violaceum with seven-bladed beta-propeller fold.
Sykorova, P., Novotna, J., Demo, G., Pompidor, G., Dubska, E., Komarek, J., Fujdiarova, E., Houser, J., Haronikova, L., Varrot, A., Shilova, N., Imberty, A., Bovin, N., Pokorna, M., Wimmerova, M.(2020) Int J Biol Macromol 152: 1113-1124
- PubMed: 31751748
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
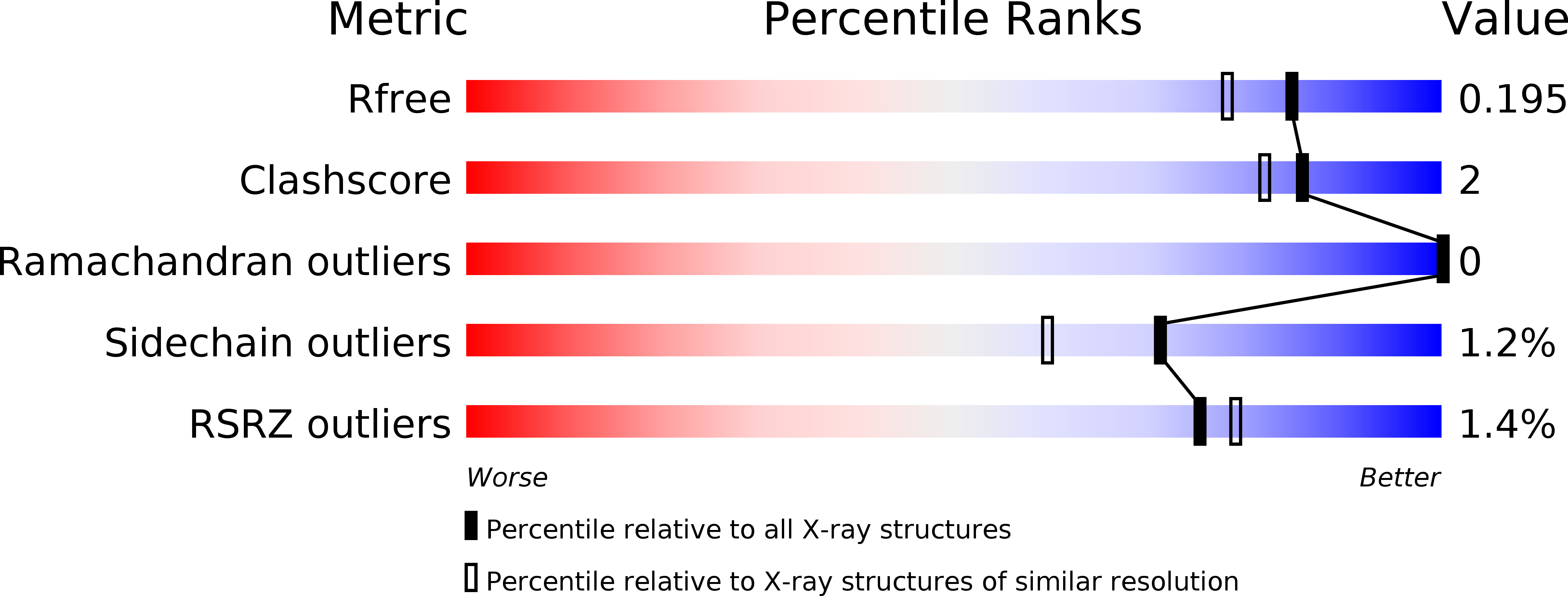
6GXR, 6GXS - PubMed Abstract:
Burkholderia pseudomallei and Chromobacterium violaceum are bacteria of tropical and subtropical soil and water that occasionally cause fatal infections in humans and animals. Microbial lectins mediate the adhesion of organisms to host cells, which is the first phase in the development of infection. Here we report the discovery of two novel lectins from the above-mentioned bacteria - BP39L and CV39L. The crystal structures revealed that the lectins possess a seven-bladed β-propeller fold. Functional studies conducted on a series of oligo- and polysaccharides confirmed the preference of BP39L for mannosylated saccharides and CV39L for rather more complex polysaccharides with a monosaccharide preference for β-l-fucose. The presented data indicate that the proteins belong to a currently unknown family of lectins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic; Central European Institute of Technology, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic.