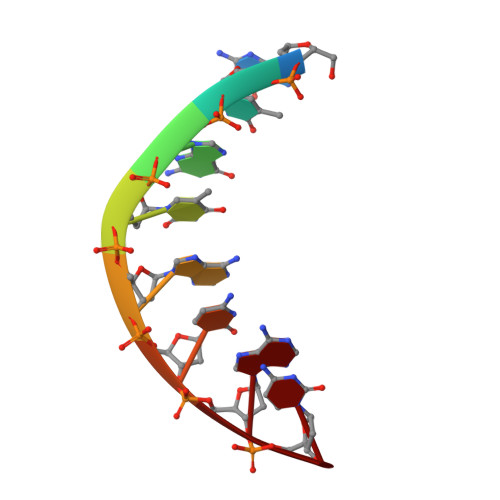
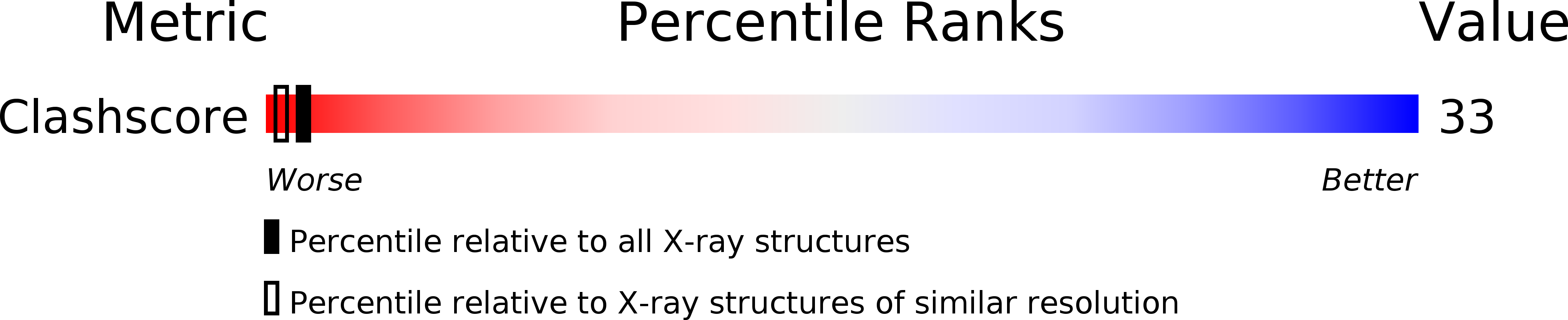Base only binding of spermine in the deep groove of the A-DNA octamer d(GTGTACAC).
Jain, S., Zon, G., Sundaralingam, M.(1989) Biochemistry 28: 2360-2364
- PubMed: 2730868
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00432a002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DNS - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of a complex of spermine with the DNA octamer d(GTGTACAC) has been determined at 2.0-A resolution. The alternating sequence adopts an A-DNA conformation with a novel purine-purine extra-Watson-Crick hydrogen bond involving the central guanine G3 (G11) and adenine A13 (A5) in the deep groove. The oligocation spermine binds in the floor of the deep groove by interacting with the bases and assumes an S-shape. Its dyad is coincident with that of the DNA, reminiscent of repressor binding to B-DNA. The terminal and central ammonium groups of the top half of spermine form hydrogen-bonding interactions to the 5'-bases, GTG, of one strand; then the spermine winds across the groove to interact with the corresponding set of bases on the other strand. The methylene groups of spermine form a hydrophobic cluster with the methyl groups of the thymines and the O6 atoms of the guanines of the TGT sequences on either side of the dyad. The observed mode of binding of spermine to A-DNA can serve as a model for deep groove binding in RNA and DNA-RNA hybrids that show a propensity also for the A-conformation. It will be of interest to see if base binding of spermine to DNA is involved in the regulation of gene expression, since spermine and other oligocations are ubiquitous in cells and their concentration is coupled to stages in cell cycle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, College of Agricultural and Life Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison 53706.