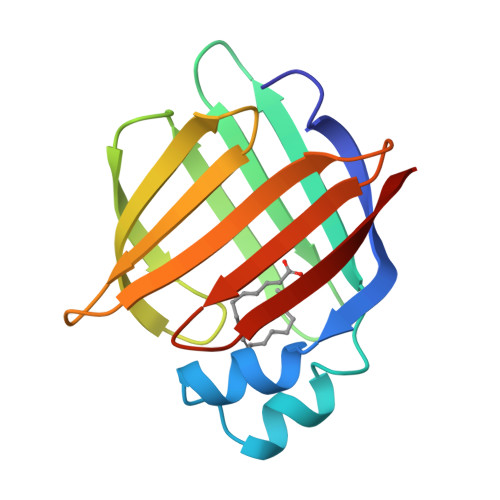
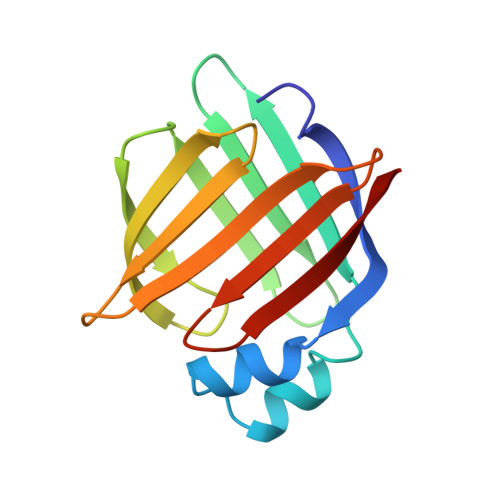
Structural studies on human muscle fatty acid binding protein at 1.4 A resolution: binding interactions with three C18 fatty acids.
Young, A.C., Scapin, G., Kromminga, A., Patel, S.B., Veerkamp, J.H., Sacchettini, J.C.(1994) Structure 2: 523-534
- PubMed: 7922029
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00052-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HMR, 1HMS, 1HMT - PubMed Abstract:
Muscle fatty acid binding protein (M-FABP) is one of a family of cytosolic lipid-binding proteins involved in fatty acid processing. In order to investigate the precise interactions between M-FABP and its ligands and to understand the structural basis of differential binding affinity, we have compared the structures of M-FABP in complex with three C18 fatty acids. We describe the crystal structures of M-FABP in complex with n-octadecanoate (stearate), trans-delta 9-octadecenoate (elaidate) and cis-delta 9-octadecenoate (oleate). These structures were refined using least-squares positional and anisotropic temperature factor refinement to final R-factors of 11.4%, 12.1% and 13.2% respectively for all the data between 8.0 A and 1.4 A resolution. Stearate, elaidate and oleate each adopt highly similar U-shaped conformations when they bind to M-FABP within a large interior binding cavity, which also contains 13 ordered water molecules. The atomic structure of the protein is virtually identical, regardless of the nature of the bound ligand. The fatty acid is thought to enter the interior cavity of the protein via a portal in its surface while interior solvent is released through a secondary opening. The ligand affinity can be correlated with the conformational energy and the solubility of the bound ligand.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York 10461.