Structural basis for recognition by an in vitro evolved affibody.
Hogbom, M., Eklund, M., Nygren, P.A., Nordlund, P.(2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 3191-3196
- PubMed: 12604795
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0436100100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LP1 - PubMed Abstract:
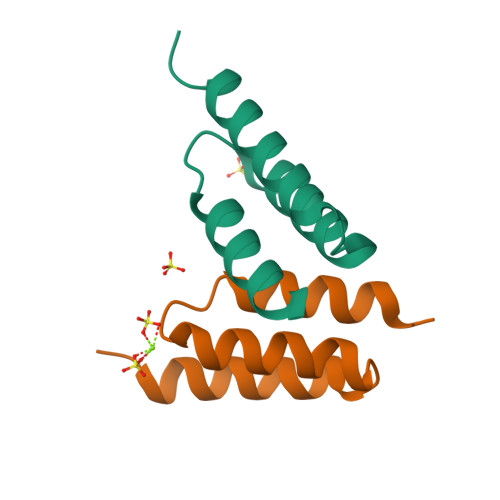
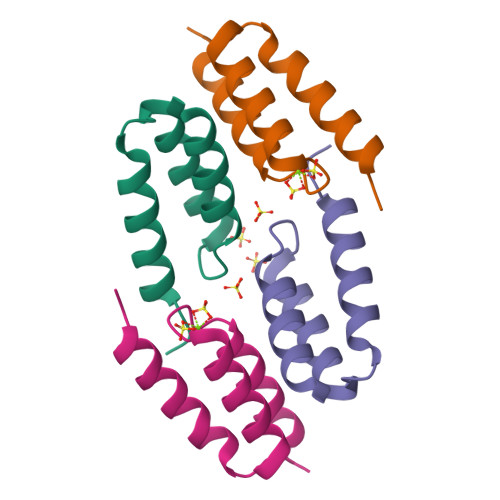
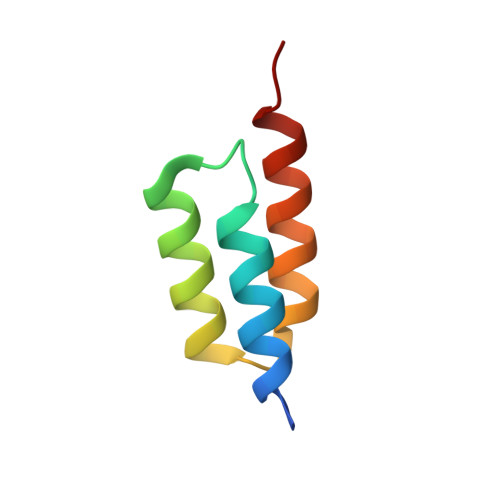
The broad binding repertoire of antibodies has permitted their use in a wide range of applications. However, some uses of antibodies are precluded due to limitations in the efficiency of antibody generation. In vitro evolved binding proteins, selected from combinatorial libraries generated around various alternative structural scaffolds, are promising alternatives to antibodies. We have solved the crystal structure of a complex of an all alpha-helical in vitro selected binding protein (affibody) bound to protein Z, an IgG Fc-binding domain derived from staphylococcal protein A. The structure of the complex reveals an extended and complementary binding surface with similar properties to protein-antibody interactions. The surface region of protein Z recognized by the affibody is strikingly similar to the one used for IgG(1) Fc binding, suggesting that this surface contains potential hot-spots for binding. The implications of the selected affibody binding-mode for its application as a universal binding protein are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University, Roslagstullsbacken 15, Albanova University Center, SE-10691 Stockholm, Sweden.