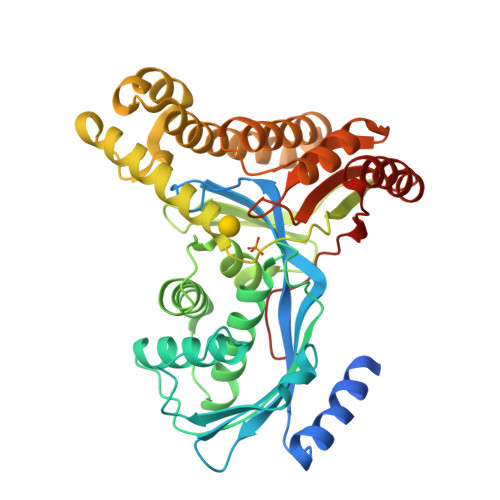
Molecular Structure of Galactokinase
Thoden, J.B., Holden, H.M.(2003) J Biological Chem 278: 33305-33311
- PubMed: 12796487
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304789200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PIE - PubMed Abstract:
Galactokinase plays a key role in normal galactose metabolism by catalyzing the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of alpha-D-galactose to galactose 1-phosphate. In humans, mutations in the galactokinase gene can lead to the diseased state referred to as Type II galactosemia. Here we describe the three-dimensional structure of galactokinase from Lactococcus lactis determined to 2.1-A resolution. As expected from amino acid sequence alignments, galactokinase adopts a similar topology to that observed for members of the GHMP superfamily. The N-terminal domain is characterized by a five-stranded mixed beta-sheet while the C-terminal motif is dominated by two distinct four-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheets. The structure was solved in the presence of alpha-D-galactose and inorganic phosphate. These ligands are wedged between the N- and C-terminal domains. Amino acid side chains responsible for anchoring the sugar ligand to the protein include Arg36, Glu42, Asp45, Asp183, and Tyr233. Both Arg36 and Asp183 are strictly conserved in the amino acid sequences available in the literature thus far for galactokinases. Interestingly, the carboxylate side chain of Asp183 is positioned within 3.5 A of the C-1 hydroxyl group of galactose, whereas the guanidinium group of Arg36 is situated between both the C-1 hydroxyl group and the inorganic phosphate. Most likely these residues play key roles in catalysis. The structure of galactokinase described here serves as a model for understanding the functional consequences of point mutations known to result in Type II galactosemia in humans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 53706, USA.