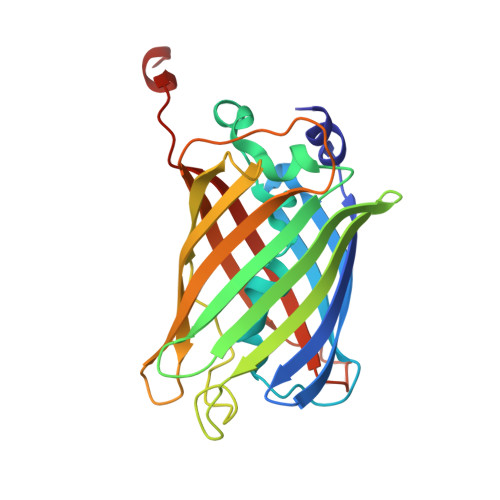
Mechanism and energetics of green fluorescent protein chromophore synthesis revealed by trapped intermediate structures.
Barondeau, D.P., Putnam, C.D., Kassmann, C.J., Tainer, J.A., Getzoff, E.D.(2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 12111-12116
- PubMed: 14523232
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2133463100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QXT, 1QY3, 1QYF, 1QYO, 1QYQ - PubMed Abstract:
Green fluorescent protein has revolutionized cell labeling and molecular tagging, yet the driving force and mechanism for its spontaneous fluorophore synthesis are not established. Here we discover mutations that substantially slow the rate but not the yield of this posttranslational modification, determine structures of the trapped precyclization intermediate and oxidized postcyclization states, and identify unanticipated features critical to chromophore maturation. The protein architecture contains a dramatic approximately 80 degrees bend in the central helix, which focuses distortions at G67 to promote ring formation from amino acids S65, Y66, and G67. Significantly, these distortions eliminate potential helical hydrogen bonds that would otherwise have to be broken at an energetic cost during peptide cyclization and force the G67 nitrogen and S65 carbonyl oxygen atoms within van der Waals contact in preparation for covalent bond formation. Further, we determine that under aerobic, but not anaerobic, conditions the Gly-Gly-Gly chromophore sequence cyclizes and incorporates an oxygen atom. These results lead directly to a conjugation-trapping mechanism, in which a thermodynamically unfavorable cyclization reaction is coupled to an electronic conjugation trapping step, to drive chromophore maturation. Moreover, we propose primarily electrostatic roles for the R96 and E222 side chains in chromophore formation and suggest that the T62 carbonyl oxygen is the base that initiates the dehydration reaction. Our molecular mechanism provides the basis for understanding and eventually controlling chromophore creation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, The Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.