Structure of the Chlamydia protein CADD reveals a redox enzyme that modulates host cell apoptosis.
Schwarzenbacher, R., Stenner-Liewen, F., Liewen, H., Robinson, H., Yuan, H., Bossy-Wetzel, E., Reed, J.C., Liddington, R.C.(2004) J Biological Chem 279: 29320-29324
- PubMed: 15087448
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401268200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RCW - PubMed Abstract:
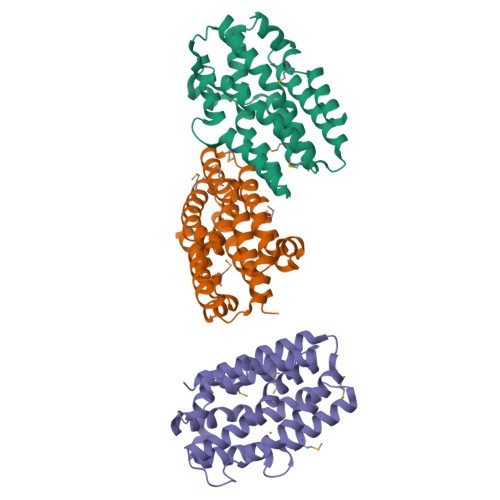
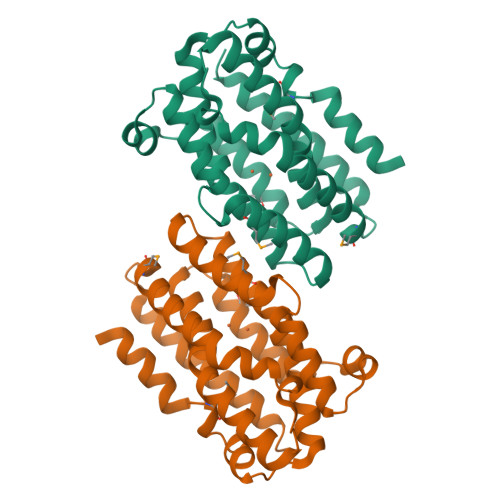
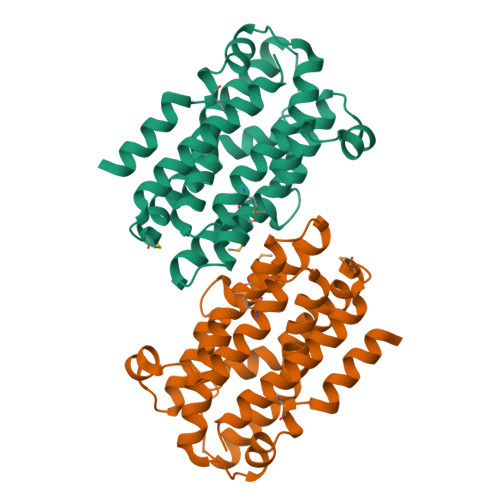
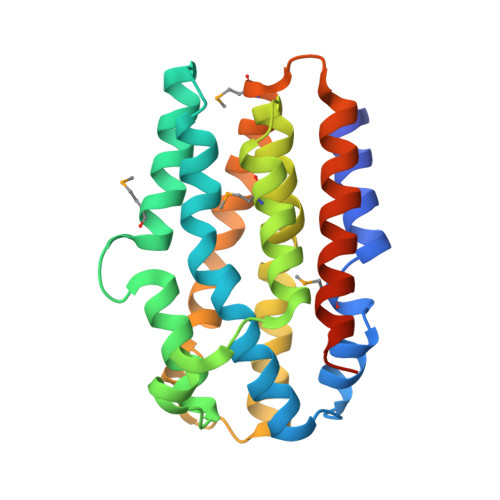
The Chlamydia protein CADD (Chlamydia protein associating with death domains) has been implicated in the modulation of host cell apoptosis via binding to the death domains of tumor necrosis factor family receptors. Transfection of CADD into mammalian cells induces apoptosis. Here we present the CADD crystal structure, which reveals a dimer of seven-helix bundles. Each bundle contains a di-iron center adjacent to an internal cavity, forming an active site similar to that of methane mono-oxygenase hydrolase. We further show that CADD mutants lacking critical metal-coordinating residues are substantially less effective in inducing apoptosis but retain their ability to bind to death domains. We conclude that CADD is a novel redox protein toxin unique to Chlamydia species and propose that both its redox activity and death domain binding ability are required for its biological activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Burnham Institute, La Jolla, California 92037, USA.