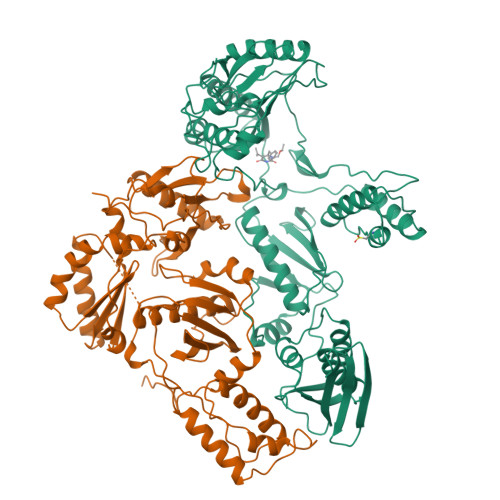
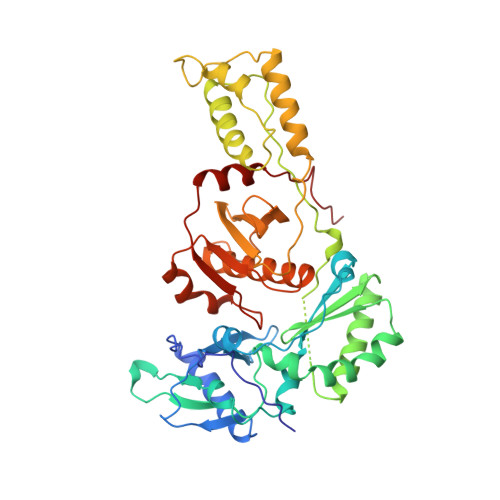
Complexes of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with inhibitors of the HEPT series reveal conformational changes relevant to the design of potent non-nucleoside inhibitors.
Hopkins, A.L., Ren, J., Esnouf, R.M., Willcox, B.E., Jones, E.Y., Ross, C., Miyasaka, T., Walker, R.T., Tanaka, H., Stammers, D.K., Stuart, D.I.(1996) J Med Chem 39: 1589-1600
- PubMed: 8648598
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm960056x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RT1, 1RT2 - PubMed Abstract:
Crystal structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) complexed with a range of chemically diverse non-nucleoside inhibitors (NNIs) have shown a single pocket in which the inhibitors bind and details of the inhibitor-protein interactions. To delineate the structural requirements for an effective inhibitor, we have determined the structures of three closely related NNIs which vary widely in their potencies. Crystal structures of HIV-1 RT complexed with two very potent inhibitors, MKC-442 and TNK-651, at 2.55 angstroms resolution complement our previous analysis of the complex with the less effective inhibitor, HEPT. These structures reveal conformational changes which correlate with changes in potency. We suggest that a major determinant of increased potency in the analogues of HEPT is an improved interaction between residue Tyr181 in the protein and the 6-benzyl ring of the inhibitors which stabilizes the structure of the complex. This arises through a conformational switching of the protein structure triggered by the steric bulk of the 5-substituent of the inhibitor pyrimidine ring.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, Rex Richards Building, Oxford, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: