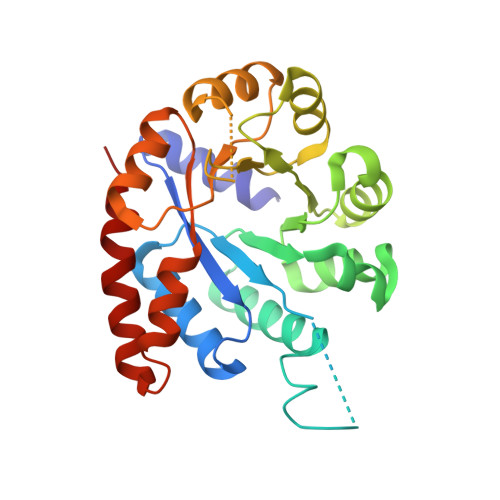
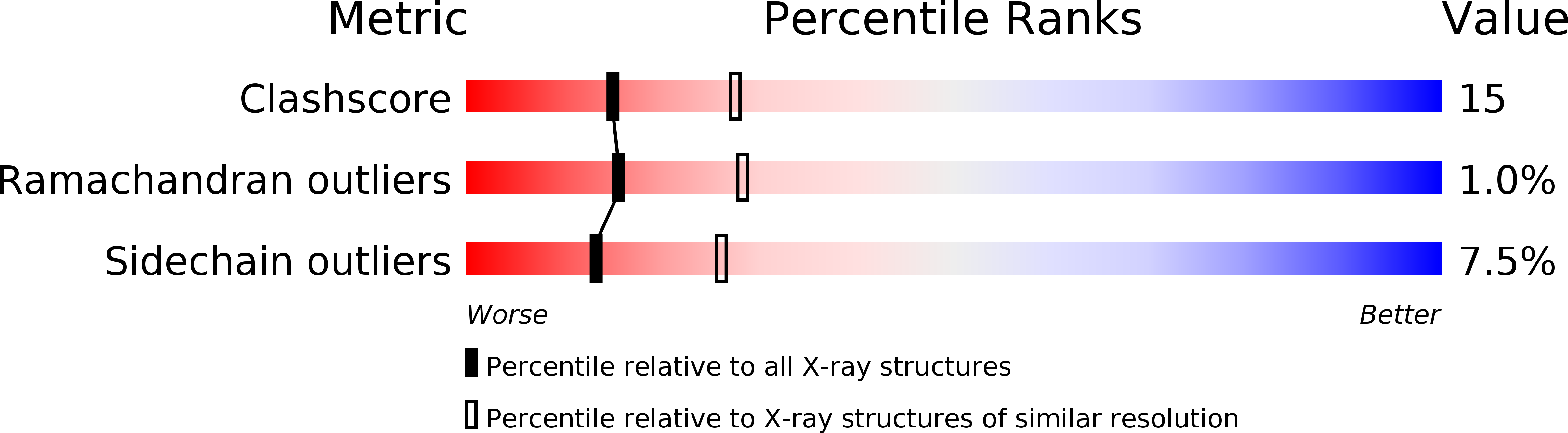Conformational Changes in the alpha-Subunit Coupled to Binding of the beta(2)-Subunit of Tryptophan Synthase from Escherichia coli: Crystal Structure of the Tryptophan Synthase alpha-Subunit Alon
Nishio, K., Morimoto, Y., Ishizuka, M., Ogasahara, K., Tsukihara, T., Yutani, K.(2005) Biochemistry 44: 1184-1192
- PubMed: 15667212
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi047927m
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1V7Y, 1WQ5 - PubMed Abstract:
When the tryptophan synthase alpha- and beta(2)-subunits combine to form the alpha(2)beta(2)-complex, the enzymatic activity of each subunit is stimulated by 1-2 orders of magnitude. To elucidate the structural basis of this mutual activation, it is necessary to determine the structures of the alpha- and beta-subunits alone and together with the alpha(2)beta(2)-complex. The crystal structures of the tryptophan synthase alpha(2)beta(2)-complex from Salmonella typhimurium (Stalpha(2)beta(2)-complex) have already been reported. However, the structures of the subunit alone from mesophiles have not yet been determined. The structure of the tryptophan synthase alpha-subunit alone from Escherichia coli (Ecalpha-subunit) was determined by an X-ray crystallographic analysis at 2.3 A, which is the first report on the subunits alone from the mesophiles. The biggest difference between the structures of the Ecalpha-subunit alone and the alpha-subunit in the Stalpha(2)beta(2)-complex (Stalpha-subunit) was as follows. Helix 2' in the Stalpha-subunit, including an active site residue (Asp60), was changed to a flexible loop in the Ecalpha-subunit alone. The conversion of the helix to a loop resulted in the collapse of the correct active site conformation. This region is also an important part for the mutual activation in the Stalpha(2)beta(2)-complex and interaction with the beta-subunit. These results suggest that the formation of helix 2'that is essential for the stimulation of the enzymatic activity of the alpha-subunit is constructed by the induced-fit mode involved in conformational changes upon interaction between the alpha- and beta-subunits. This also confirms the prediction of the conformational changes based on the thermodynamic analysis for the association between the alpha- and beta-subunits.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, 3-2 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.