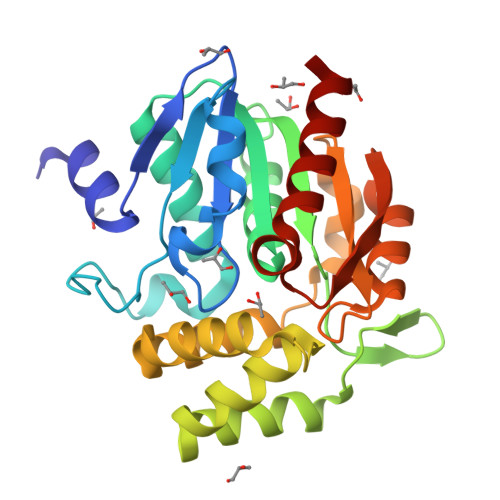
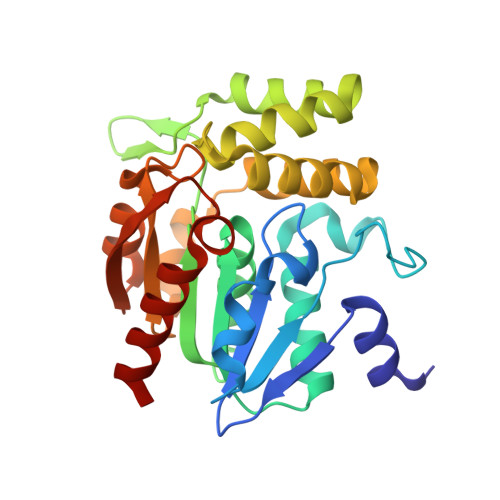
Crystal structures of RsbQ, a stress-response regulator in Bacillus subtilis
Kaneko, T., Tanaka, N., Kumasaka, T.(2005) Protein Sci 14: 558-565
- PubMed: 15632289
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.041170005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WOM, 1WPR - PubMed Abstract:
Growth-limiting stresses in bacteria induce the general stress response to protect the cells against future stresses. Energy stress caused by starvation conditions in Bacillus subtilis is transmitted to the sigma(B) transcription factor by stress-response regulators. RsbP, a positive regulator, is a phosphatase containing a PAS (Per-ARNT-Sim) domain and requires catalytic function of a putative alpha/beta hydrolase, RsbQ, to be activated. These two proteins have been found to interact with each other. We determined the crystal structures of RsbQ in native and inhibitor-bound forms to investigate why RsbP requires RsbQ. These structures confirm that RsbQ belongs to the alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily. Since the catalytic triad is buried inside the molecule due to the closed conformation, the active site is constructed as a hydrophobic cavity that is nearly isolated from the solvent. This suggests that RsbQ has specificity for a hydrophobic small compound rather than a macromolecule such as RsbP. Moreover, structural comparison with other alpha/beta hydrolases demonstrates that a unique loop region of RsbQ is a likely candidate for the interaction site with RsbP, and the interaction might be responsible for product release by operating the hydrophobic gate equipped between the cavity and the solvent. Our results support the possibility that RsbQ provides a cofactor molecule for the mature functionality of RsbP.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan.