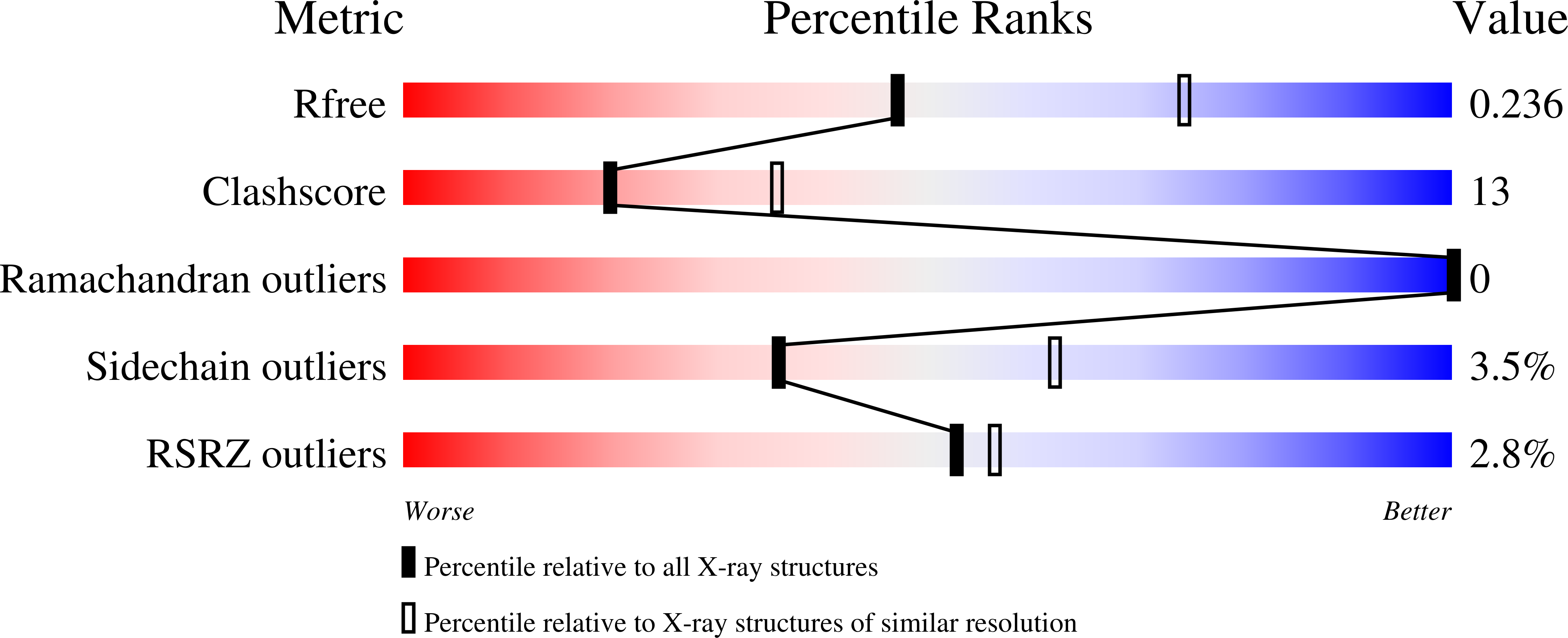
Crystal structures of GMP kinase in complex with ganciclovir monophosphate and Ap5G.
Hible, G., Daalova, P., Gilles, A.M., Cherfils, J.(2006) Biochimie 88: 1157-1164
- PubMed: 16690197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.04.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2F3R, 2F3T - PubMed Abstract:
Guanosine monophosphate kinases (GMPK), by catalyzing the phosphorylation of GMP or dGMP, are of dual potential in assisting the activation of anti-viral prodrugs or as candidates for antibiotic strategies. Human GMPK is an obligate step for the activation of acyclic guanosine analogs, such as ganciclovir, which necessitate efficient phosphorylation, while GMPK from bacterial pathogens, in which this enzyme is essential, are potential targets for therapeutic inhibition. Here we analyze these two aspects of GMPK activity with the crystal structures of Escherichia coli GMPK in complex with ganciclovir-monophosphate (GCV-MP) and with a bi-substrate inhibitor, Ap5G. GCV-MP binds as GMP to the GMP-binding domain, which is identical in E. coli and human GMPKs, but unlike the natural substrate fails to stabilize the closed, catalytically-competent conformation of this domain. Comparison with GMP- and GDP-bound GMPK structures identifies the 2'hydroxyl of the ribose moiety as responsible for hooking the GMP-binding domain onto the CORE domain. Absence of this hydroxyl in GCV-MP impairs the stabilization of the active conformation, and explains why GCV-MP is phosphorylated less efficiently than GMP, but as efficiently as dGMP. In contrast, Ap5G is an efficient inhibitor of GMPK. The crystal structure shows that Ap5G locks an incompletely closed conformation of the enzyme, in which the adenine moiety is located outside its expected binding site. Instead, it binds at a subunit interface that is unique to the bacterial enzyme, which is in equilibrium between a dimeric and an hexameric form in solution. This suggests that inhibitors could be designed to bind at this interface such as to prevent nucleotide-induced domain closure. Altogether, these complexes point to domain motions as critical components to be evaluated in therapeutic strategies targeting NMP kinases, with opposite effects depending on whether efficient phosphorylation or inhibition is being sought after.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire d'Enzymologie et Biochimie Structurales, bâtiment 34, CNRS, avenue de la Terrasse, 91198 Gif sur Yvette cedex, France.