Fragment Based Lead Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors for the Epha4 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase.
Van Linden, O.P., Farenc, C.J.A., Zoutman, W.H., Hameetman, L., Wijtmans, M., Leurs, R., Tensen, C.P., Siegal, G., De Esch, I.J.(2012) Eur J Med Chem 47: 493
- PubMed: 22137457
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.11.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XYU - PubMed Abstract:
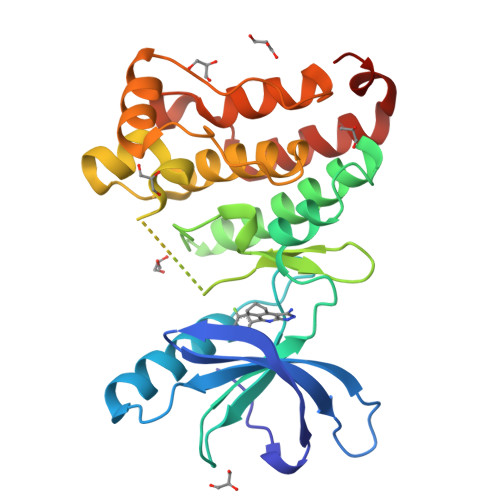
The in silico identification, optimization and crystallographic characterization of a 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]isoquinolin-1-amine scaffold as an inhibitor for the EPHA4 receptor tyrosine kinase is described. A database containing commercially available compounds was subjected to an in silico screening procedure which was focused on finding novel, EPHA4 hinge binding fragments. This resulted in the identification of 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]isoquinolin-1-amine derivatives as EPHA4 inhibitors. Hit exploration yielded a compound with 2 μM (IC(50)) affinity for the EPHA4 receptor tyrosine kinase domain. Soaking experiments into a crystal of the EPHA4 kinase domain gave a 2.11Å X-ray structure of the EPHA4 - inhibitor complex, which confirmed the binding mode of the scaffold as proposed by the initial in silico work. The results underscore the strength of fragment based in silico screening as a tool for the discovery of novel lead compounds as small molecule kinase inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Leiden/Amsterdam Center for Drug Research (LACDR), Division of Medicinal Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, VU University Amsterdam, De Boelelaan 1083, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands.