Structural analysis of arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase from Bacteroides fragilis and functional implications.
Chiu, H.J., Grant, J.C., Farr, C.L., Jaroszewski, L., Knuth, M.W., Miller, M.D., Elsliger, M.A., Deacon, A.M., Godzik, A., Lesley, S.A., Wilson, I.A.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 2640-2651
- PubMed: 25286848
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714017052
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ETN - PubMed Abstract:
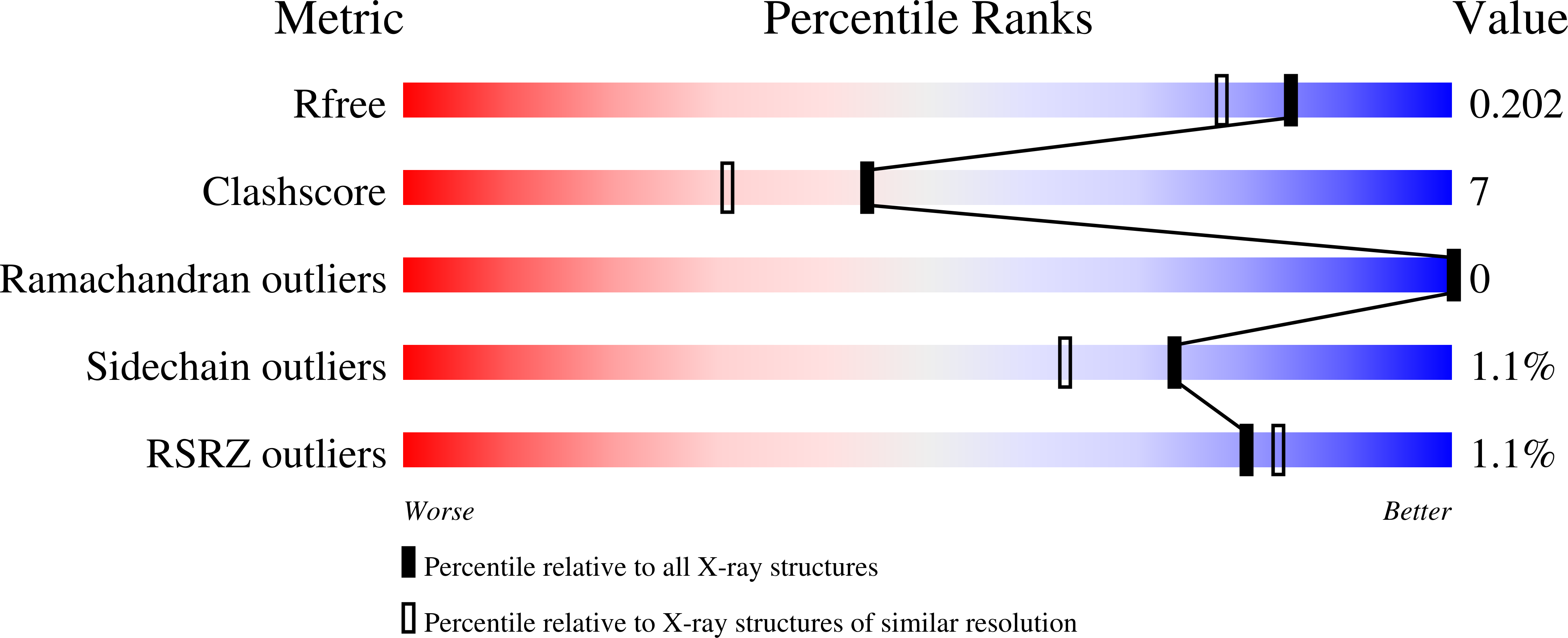
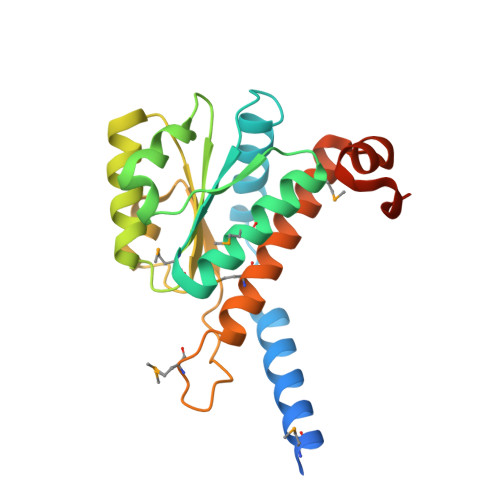
The crystal structure of arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase (API) from Bacteroides fragilis (bfAPI) was determined at 1.7 Å resolution and was found to be a tetramer of a single-domain sugar isomerase (SIS) with an endogenous ligand, CMP-Kdo (cytidine 5'-monophosphate-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate), bound at the active site. API catalyzes the reversible isomerization of D-ribulose 5-phosphate to D-arabinose 5-phosphate in the first step of the Kdo biosynthetic pathway. Interestingly, the bound CMP-Kdo is neither the substrate nor the product of the reaction catalyzed by API, but corresponds to the end product in the Kdo biosynthetic pathway and presumably acts as a feedback inhibitor for bfAPI. The active site of each monomer is located in a surface cleft at the tetramer interface between three monomers and consists of His79 and His186 from two different adjacent monomers and a Ser/Thr-rich region, all of which are highly conserved across APIs. Structure and sequence analyses indicate that His79 and His186 may play important catalytic roles in the isomerization reaction. CMP-Kdo mimetics could therefore serve as potent and specific inhibitors of API and provide broad protection against many different bacterial infections.
Organizational Affiliation:
Joint Center for Structural Genomics, http://www.jcsg.org, USA.