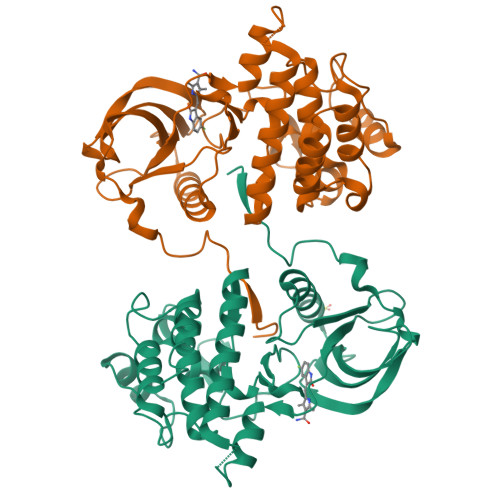
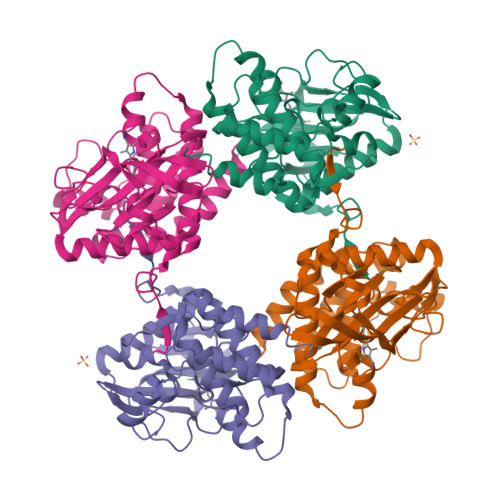
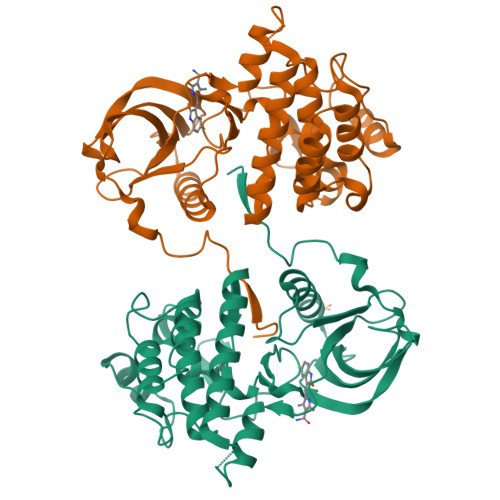
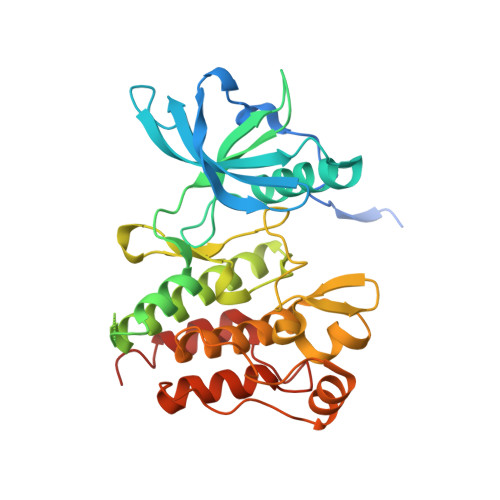
KIT kinase mutants show unique mechanisms of drug resistance to imatinib and sunitinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients.
Gajiwala, K.S., Wu, J.C., Christensen, J., Deshmukh, G.D., Diehl, W., DiNitto, J.P., English, J.M., Greig, M.J., He, Y.A., Jacques, S.L., Lunney, E.A., McTigue, M., Molina, D., Quenzer, T., Wells, P.A., Yu, X., Zhang, Y., Zou, A., Emmett, M.R., Marshall, A.G., Zhang, H.M., Demetri, G.D.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 1542-1547
- PubMed: 19164557
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812413106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3G0E, 3G0F - PubMed Abstract:
Most gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) exhibit aberrant activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) KIT. The efficacy of the inhibitors imatinib mesylate and sunitinib malate in GIST patients has been linked to their inhibition of these mutant KIT proteins. However, patients on imatinib can acquire secondary KIT mutations that render the protein insensitive to the inhibitor. Sunitinib has shown efficacy against certain imatinib-resistant mutants, although a subset that resides in the activation loop, including D816H/V, remains resistant. Biochemical and structural studies were undertaken to determine the molecular basis of sunitinib resistance. Our results show that sunitinib targets the autoinhibited conformation of WT KIT and that the D816H mutant undergoes a shift in conformational equilibrium toward the active state. These findings provide a structural and enzymologic explanation for the resistance profile observed with the KIT inhibitors. Prospectively, they have implications for understanding oncogenic kinase mutants and for circumventing drug resistance.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departments of Structural and Computational Biology, Cancer Biology, and Biochemical Pharmacology, Pfizer Global Research and Development, 10777 Science Center Drive, La Jolla, CA 92121, USA.