Discovery, SAR, and pharmacokinetics of a novel 3-Hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one series of potent D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors
Duplantier, A.J., Becker, S.L., Bohanon, M.J., Borzilleri, K.A., Chrunyk, B.A., Downs, J.T., Hu, L.Y., El-Kattan, A., James, L.C., Liu, S., Lu, J., Maklad, N., Mansour, M.N., Mente, S., Piotrowski, M.A., Sakya, S.M., Sheehan, S., Steyn, S.J., Strick, C.A., Williams, V.A., Zhang, L.(2009) J Med Chem 52: 3576-3585
- PubMed: 19438227
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm900128w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3G3E - PubMed Abstract:
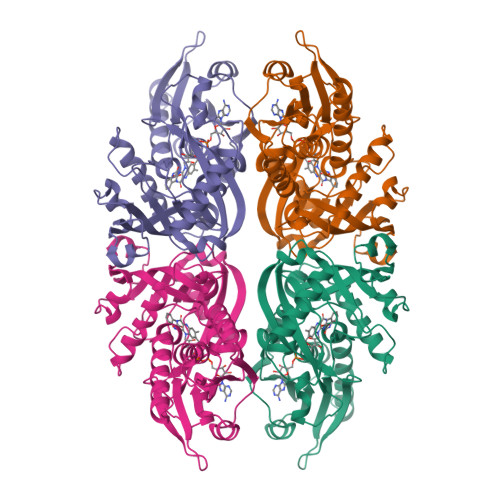
3-Hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one (2) was discovered by high throughput screening in a functional assay to be a potent inhibitor of human DAAO, and its binding affinity was confirmed in a Biacore assay. Cocrystallization of 2 with the human DAAO enzyme defined the binding site and guided the design of new analogues. The SAR, pharmacokinetics, brain exposure, and effects on cerebellum D-serine are described. Subsequent evaluation against the rat DAAO enzyme revealed a divergent SAR versus the human enzyme and may explain the high exposures of drug necessary to achieve significant changes in rat or mouse cerebellum D-serine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Pfizer Global Research and Development, Groton Laboratories, Groton, CT 06340, USA. allen.j.duplantier@pfizer.com