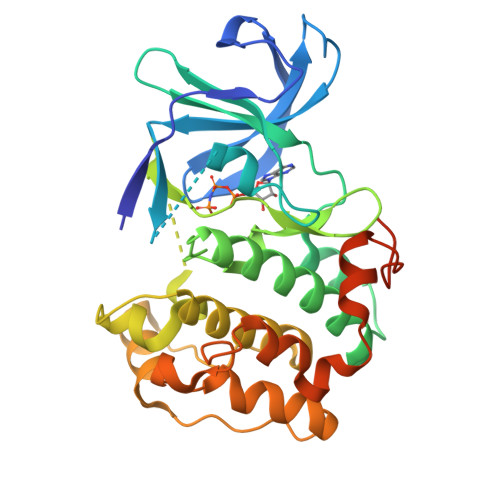
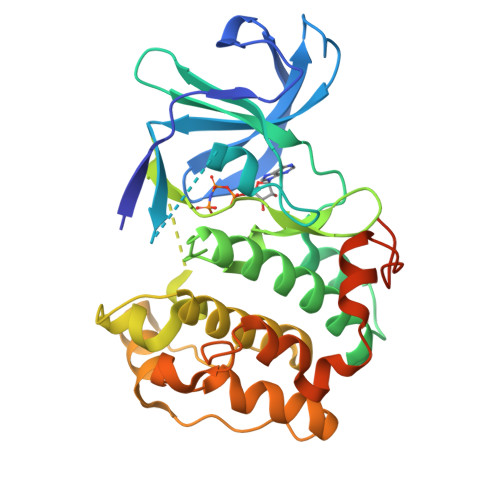
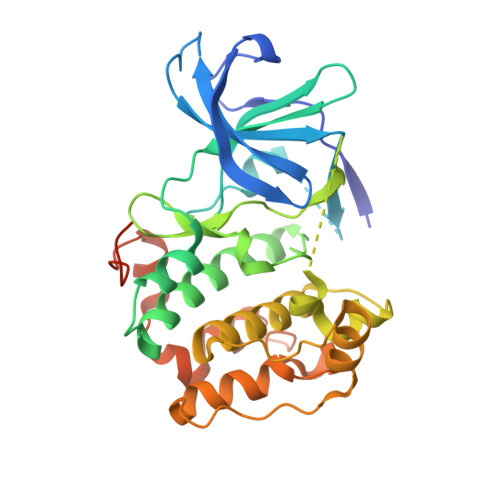
Structural diversity of the active N-terminal kinase domain of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 2
Malakhova, M., Kurinov, I., Liu, K., Zheng, D., D'Angelo, I., Shim, J.H., Steinman, V., Bode, A.M., Dong, Z.(2009) PLoS One 4: e8044-e8044
- PubMed: 19956600
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3G51 - PubMed Abstract:
The p90 ribosomal protein kinase 2 (RSK2) is a highly expressed Ser/Thr kinase activated by growth factors and is involved in cancer cell proliferation and tumor promoter-induced cell transformation. RSK2 possesses two non-identical kinase domains, and the structure of its N-terminal domain (NTD), which is responsible for phosphorylation of a variety of substrates, is unknown. The crystal structure of the NTD RSK2 was determined at 1.8 A resolution in complex with AMP-PNP. The N-terminal kinase domain adopted a unique active conformation showing a significant structural diversity of the kinase domain compared to other kinases. The NTD RSK2 possesses a three-stranded betaB-sheet inserted in the N-terminal lobe, resulting in displacement of the alphaC-helix and disruption of the Lys-Glu interaction, classifying the kinase conformation as inactive. The purified protein was phosphorylated at Ser227 in the T-activation loop and exhibited in vitro kinase activity. A key characteristic is the appearance of a new contact between Lys216 (betaB-sheet) and the beta-phosphate of AMP-PNP. Mutation of this lysine to alanine impaired both NTDs in vitro and full length RSK2 ex vivo activity, emphasizing the importance of this interaction. Even though the N-terminal lobe undergoes structural re-arrangement, it possesses an intact hydrophobic groove formed between the alphaC-helix, the beta4-strand, and the betaB-sheet junction, which is occupied by the N-terminal tail. The presence of a unique betaB-sheet insert in the N-lobe suggests a different type of activation mechanism for RSK2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular and Molecular Biology, The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, Minnesota, United States of America.