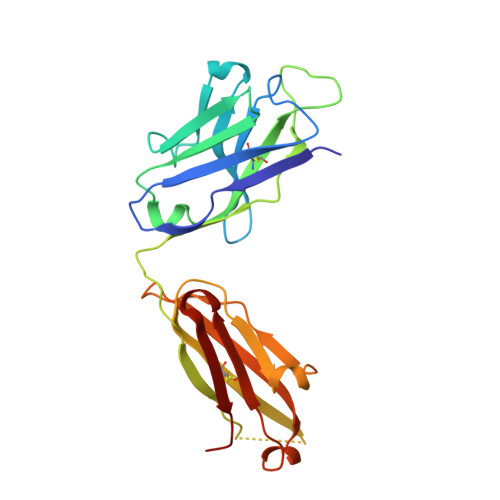
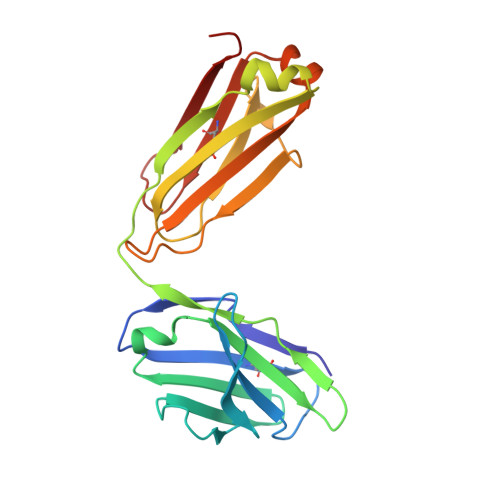
Antibody 2G12 recognizes di-mannose equivalently in domain- and nondomain-exchanged forms but only binds the HIV-1 glycan shield if domain exchanged.
Doores, K.J., Fulton, Z., Huber, M., Wilson, I.A., Burton, D.R.(2010) J Virol 84: 10690-10699
- PubMed: 20702629
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01110-10
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OAU - PubMed Abstract:
The broadly neutralizing anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) antibody 2G12 targets the high-mannose cluster on the glycan shield of HIV-1. 2G12 has a unique V(H) domain-exchanged structure, with a multivalent binding surface that includes two primary glycan binding sites. The high-mannose cluster is an attractive target for HIV-1 vaccine design, but so far, no carbohydrate immunogen has elicited 2G12-like antibodies. Important questions remain as to how this domain exchange arose in 2G12 and how this unusual event conferred unexpected reactivity against the glycan shield of HIV-1. In order to address these questions, we generated a nondomain-exchanged variant of 2G12 to produce a conventional Y/T-shaped antibody through a single amino acid substitution (2G12 I19R) and showed that, as for the 2G12 wild type (2G12 WT), this antibody is able to recognize the same Manα1,2Man motif on recombinant gp120, Candida albicans, and synthetic glycoconjugates. However, the nondomain-exchanged variant of 2G12 is unable to bind the cluster of mannose moieties on the surface of HIV-1. Crystallographic analysis of 2G12 I19R in complex with Manα1,2Man revealed an adaptable hinge between V(H) and C(H)1 that enables the V(H) and V(L) domains to assemble in such a way that the configuration of the primary binding site and its interaction with disaccharide are remarkably similar in the nondomain-exchanged and domain-exchanged forms. Together with data that suggest that very few substitutions are required for domain exchange, the results suggest potential mechanisms for the evolution of domain-exchanged antibodies and immunization strategies for eliciting such antibodies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Immunology and Microbial Science, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.