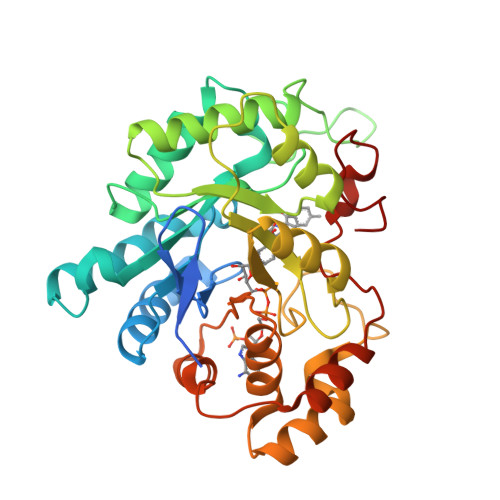
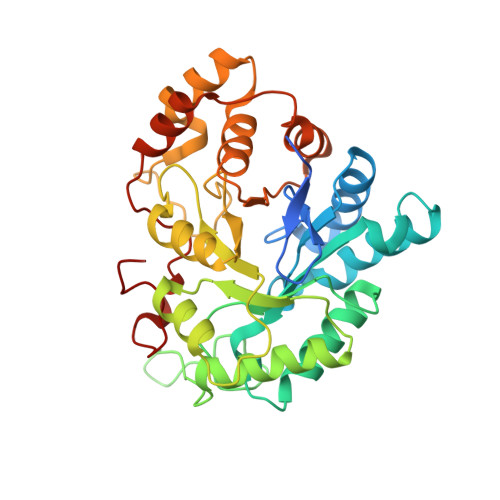
The molecular basis for inhibition of sulindac and its metabolites towards human aldose reductase.
Zheng, X., Zhang, L., Zhai, J., Chen, Y., Luo, H., Hu, X.(2012) FEBS Lett 586: 55-59
- PubMed: 22155003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.11.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RX2, 3RX3, 3RX4, 3S3G - PubMed Abstract:
Sulindac (SLD) exhibits both the highest inhibitory activity towards human aldose reductase (AR) among popular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and clear beneficial clinical effects on Type 2 diabetes. However, the molecular basis for these properties is unclear. Here, we report that SLD and its pharmacologically active/inactive metabolites, SLD sulfide and SLD sulfone, are equally effective as un-competitive inhibitors of AR in vitro. Crystallographic analysis reveals that π-π stacking favored by the distinct scaffold of SLDs is pivotal to their high AR inhibitory activities. These results also suggest that SLD sulfone could be a potent lead compound for AR inhibition in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China. huxpeng@mail.sysu.edu.cn