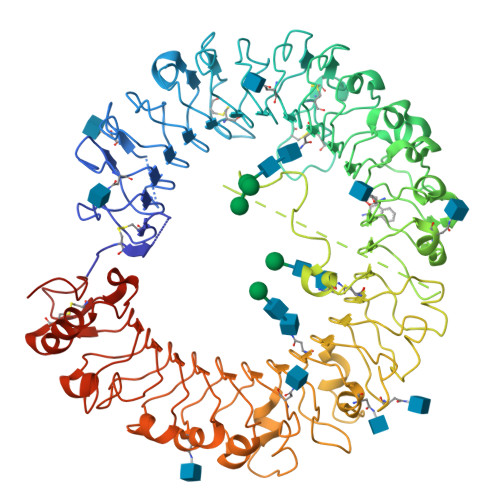
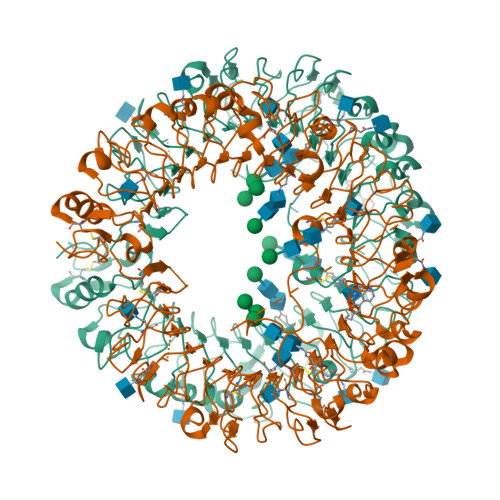
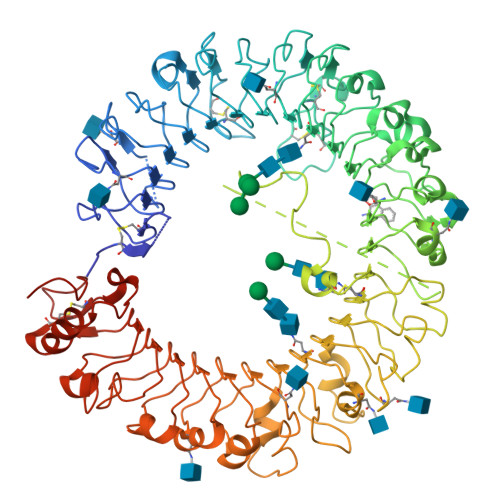
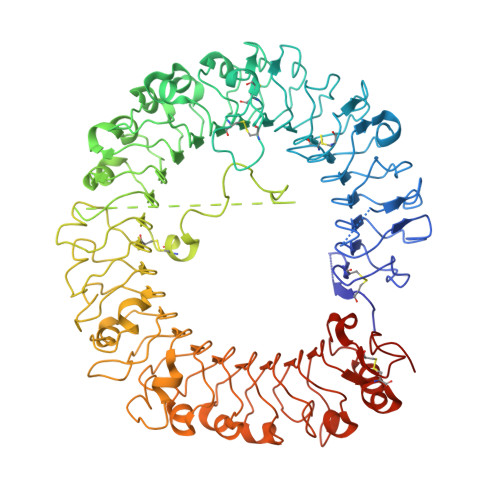
Structure-based design of novel human Toll-like receptor 8 agonists.
Kokatla, H.P., Sil, D., Tanji, H., Ohto, U., Malladi, S.S., Fox, L.M., Shimizu, T., David, S.A.(2014) ChemMedChem 9: 719-723
- PubMed: 24474703
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201300573
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WN4 - PubMed Abstract:
Toll-like receptor (TLR)-8 agonists activate adaptive immune responses by inducing robust production of T helper 1-polarizing cytokines, suggesting that TLR8-active compounds might be promising candidate vaccine adjuvants. Recently, a C2-butyl furo[2,3-c]quinoline was reported with purely TLR8 agonistic activity. This compound was successfully co-crystallized with the human TLR8 ectodomain, and the co-crystal structure revealed ligand-induced reorganization of the binding pocket of TLR8. The loss of a key hydrogen bond between the oxygen atom of the furanyl ring of the agonist and Thr 574 in TLR8 suggested that the furan ring is dispensable. Employing a disconnection strategy, 3- and 4-substituted aminoquinolines were investigated. Focused structure-based ligand design studies led to the identification of 3-pentyl-quinoline-2-amine as a novel, structurally simple, and highly potent human TLR8-specific agonist (EC50 =0.2 μM). Preliminary evaluation of this compound in ex vivo human blood assay systems revealed that it retains prominent cytokine-inducing activity. Together, these results indicate the suitability of this compound as a novel vaccine adjuvant, warranting further investigation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, University of Kansas, Multidisciplinary Research Building, Room 320D, 2030 Becker Drive, Lawrence KS 66047 (USA).