A Platform of C-type Lectin-like Receptor CLEC-2 for Binding O-Glycosylated Podoplanin and Nonglycosylated Rhodocytin
Nagae, M., Morita-Matsumoto, K., Kato, M., Kato-Kaneko, M., Kato, Y., Yamaguchi, Y.(2014) Structure 22: 1711-1721
- PubMed: 25458834
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.09.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WSR, 3WWK - PubMed Abstract:
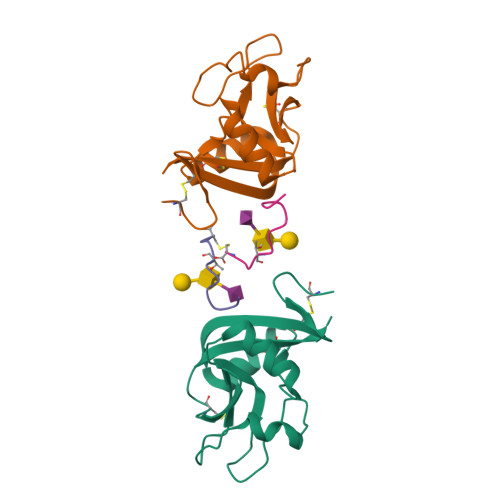
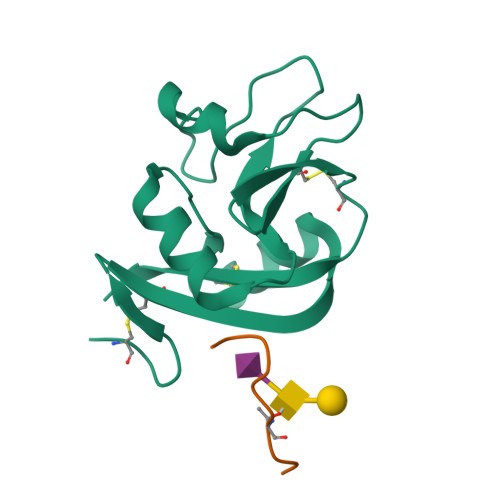
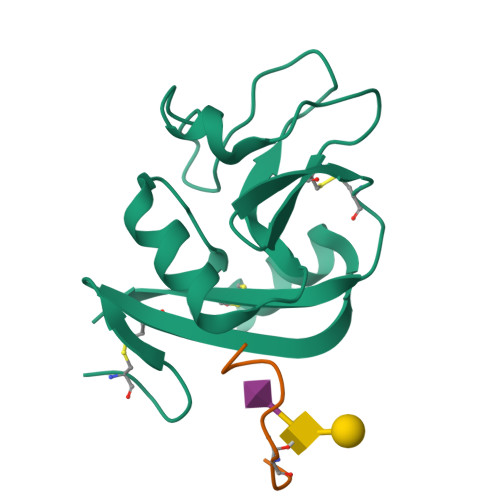
Podoplanin is a transmembrane O-glycoprotein that binds to C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (CLEC-2). The O-glycan-dependent interaction seems to play crucial roles in various biological processes, such as platelet aggregation. Rhodocytin, a snake venom, also binds to CLEC-2 and aggregates platelets in a glycan-independent manner. To elucidate the structural basis of the glycan-dependent and independent interactions, we performed comparative crystallographic studies of podoplanin and rhodocytin in complex with CLEC-2. Both podoplanin and rhodocytin bind to the noncanonical "side" face of CLEC-2. There is a common interaction mode between consecutive acidic residues on the ligands and the same arginine residues on CLEC-2. Other interactions are ligand-specific. Carboxyl groups from the sialic acid residue on podoplanin and from the C terminus of the rhodocytin α subunit interact differently at this "second" binding site on CLEC-2. The unique and versatile binding modes open a way to understand the functional consequences of CLEC-2-ligand interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Glycobiology Team, Systems Glycobiology Research Group, RIKEN-Max Planck Joint Research Center, RIKEN Global Research Cluster, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan.