Structure-based discovery of substituted 4,5'-bithiazoles as novel DNA gyrase inhibitors.
Brvar, M., Perdih, A., Renko, M., Anderluh, G., Turk, D., Solmajer, T.(2012) J Med Chem 55: 6413-6426
- PubMed: 22731783
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm300395d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DUH - PubMed Abstract:
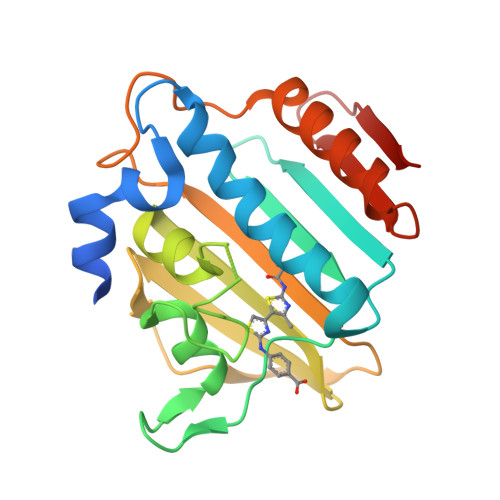
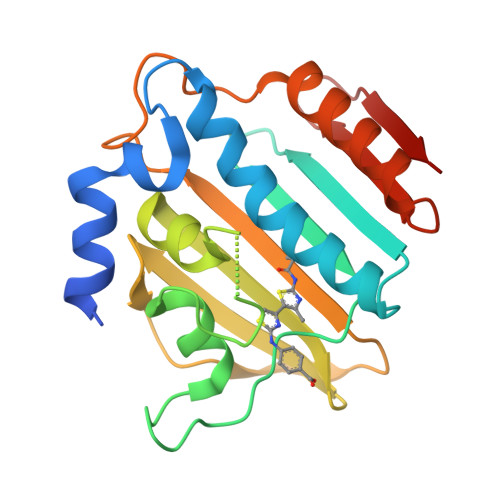
Bacterial DNA gyrase is a well-established and validated target for the development of novel antibacterials. Starting from the available structural information about the binding of the natural product inhibitor, clorobiocin, we identified a novel series of 4'-methyl-N(2)-phenyl-[4,5'-bithiazole]-2,2'-diamine inhibitors of gyrase B with a low micromolar inhibitory activity by implementing a two-step structure-based design procedure. This novel class of DNA gyrase inhibitors was extensively investigated by various techniques (differential scanning fluorimetry, surface plasmon resonance, and microscale thermophoresis). The binding mode of the potent inhibitor 18 was revealed by X-ray crystallography, confirming our initial in silico binding model. Furthermore, the high resolution of the complex structure allowed for the placement of the Gly97-Ser108 flexible loop, thus revealing its role in binding of this class of compounds. The crystal structure of the complex protein G24 and inhibitor 18 provides valuable information for further optimization of this novel class of DNA gyrase B inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Institute of Chemistry, Laboratory for Biocomputing and Bioinformatics, 1001 Ljubljana, Slovenia.