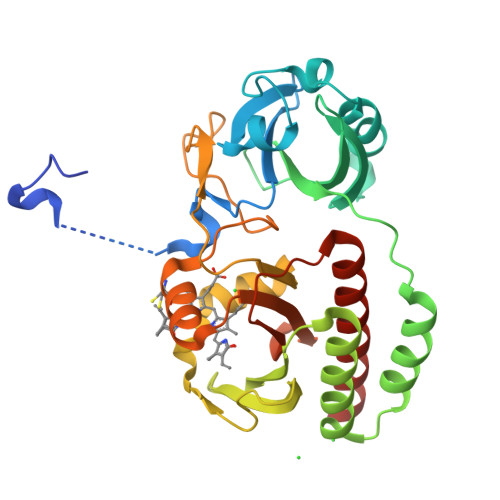
Molecular Basis of Spectral Diversity in Near-Infrared Phytochrome-Based Fluorescent Proteins.
Shcherbakova, D.M., Baloban, M., Pletnev, S., Malashkevich, V.N., Xiao, H., Dauter, Z., Verkhusha, V.V.(2015) Chem Biol 22: 1540-1551
- PubMed: 26590639
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.10.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XTQ - PubMed Abstract:
Near-infrared fluorescent proteins (NIR FPs) engineered from bacterial phytochromes (BphPs) are the probes of choice for deep-tissue imaging. Detection of several processes requires spectrally distinct NIR FPs. We developed an NIR FP, BphP1-FP, which has the most blue-shifted spectra and the highest fluorescence quantum yield among BphP-derived FPs. We found that these properties result from the binding of the biliverdin chromophore to a cysteine residue in the GAF domain, unlike natural BphPs and other BphP-based FPs. To elucidate the molecular basis of the spectral shift, we applied biochemical, structural and mass spectrometry analyses and revealed the formation of unique chromophore species. Mutagenesis of NIR FPs of different origins indicated that the mechanism of the spectral shift is general and can be used to design multicolor NIR FPs from other BphPs. We applied pairs of spectrally distinct point cysteine mutants to multicolor cell labeling and demonstrated that they perform well in model deep-tissue imaging.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Anatomy and Structural Biology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY 10461, USA.