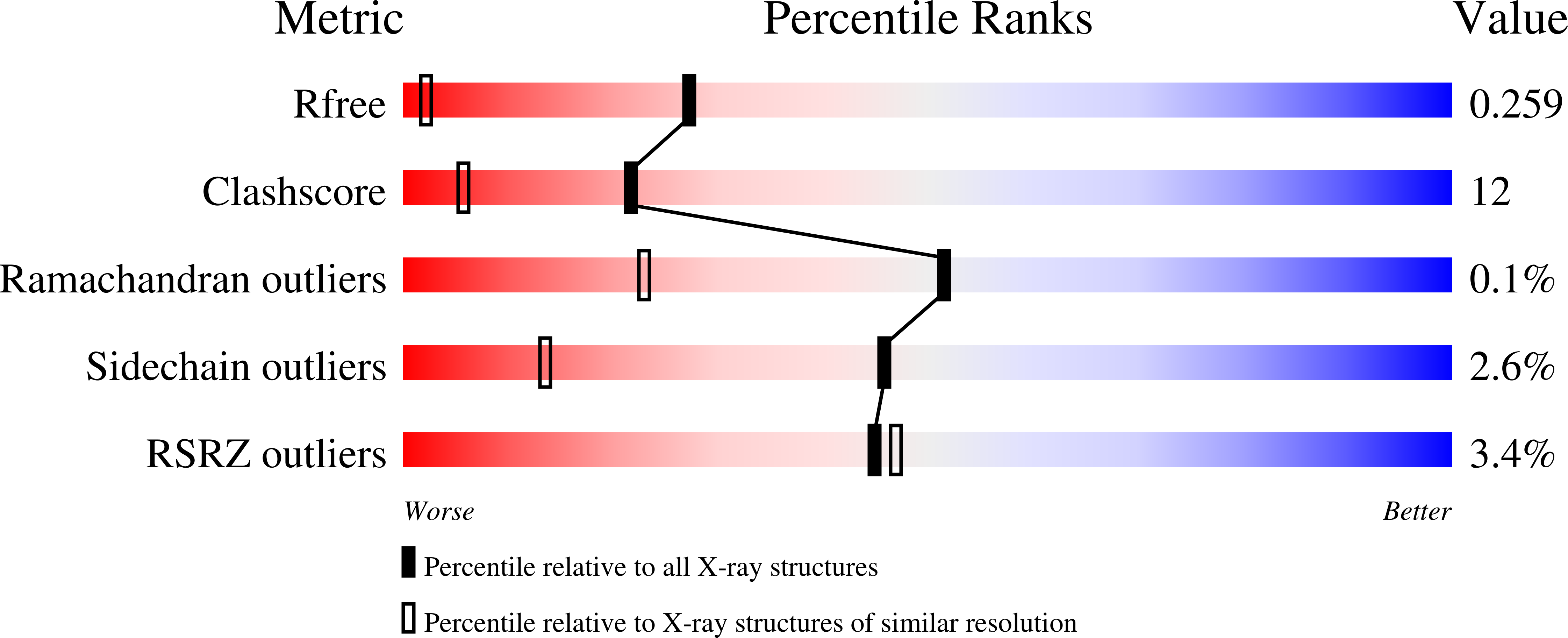
Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of N-Myristoyltransferase from Human Malaria and Leishmaniasis Parasites.
Olaleye, T.O., Brannigan, J.A., Roberts, S.M., Leatherbarrow, R.J., Wilkinson, A.J., Tate, E.W.(2014) Org Biomol Chem 12: 8132
- PubMed: 25230674
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ob01669f
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4C68, 4C7H, 4C7I - PubMed Abstract:
N-Myristoyltransferase (NMT) has been shown to be essential in Leishmania and subsequently validated as a drug target in Plasmodium. Herein, we discuss the use of antifungal NMT inhibitors as a basis for inhibitor development resulting in the first sub-micromolar peptidomimetic inhibitors of Plasmodium and Leishmania NMTs. High-resolution structures of these inhibitors with Plasmodium and Leishmania NMTs permit a comparative analysis of binding modes, and provide the first crystal structure evidence for a ternary NMT-Coenzyme A/myristoylated peptide product complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Imperial College London, London, SW7 2AZ, UK. e.tate@imperial.ac.uk.