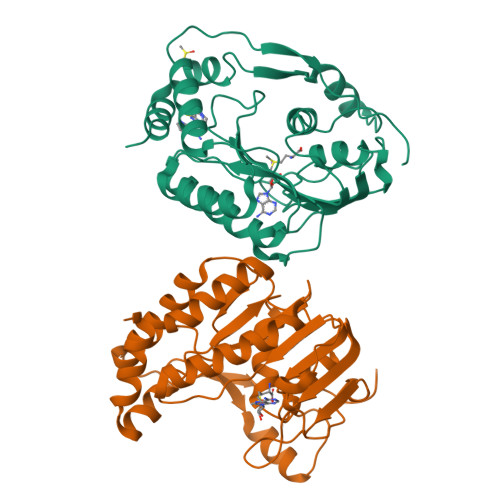
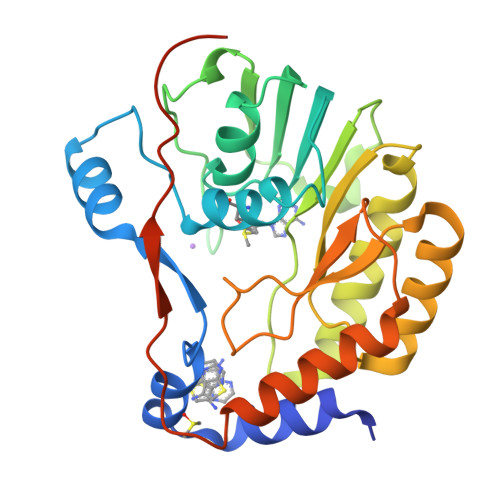
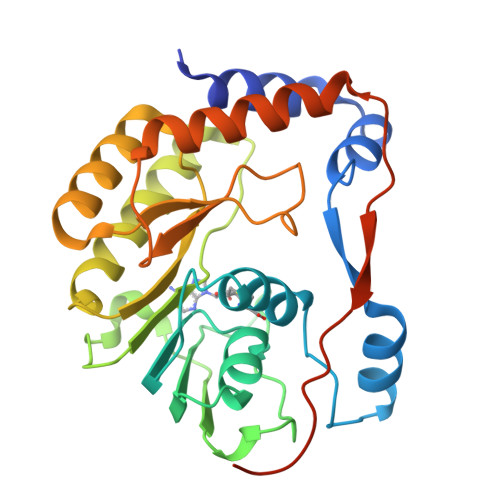
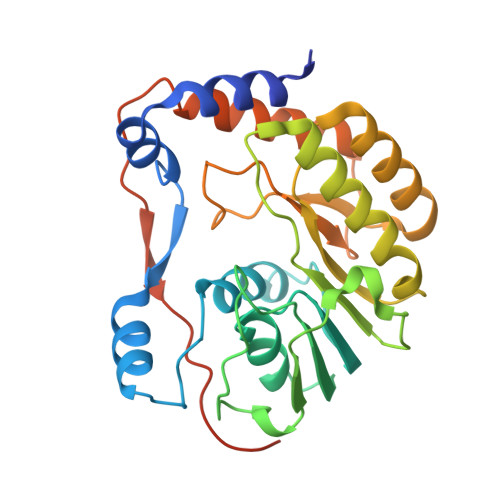
Assessment of Dengue Virus Helicase and Methyltransferase as Targets for Fragment-Based Drug Discovery.
Coutard, B., Decroly, E., Li, C., Sharff, A., Lescar, J., Bricogne, G., Barral, K.(2014) Antiviral Res 106: 61
- PubMed: 24704437
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.03.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CTJ, 4CTK - PubMed Abstract:
Seasonal and pandemic flaviviruses continue to be leading global health concerns. With the view to help drug discovery against Dengue virus (DENV), a fragment-based experimental approach was applied to identify small molecule ligands targeting two main components of the flavivirus replication complex: the NS3 helicase (Hel) and the NS5 mRNA methyltransferase (MTase) domains. A library of 500 drug-like fragments was first screened by thermal-shift assay (TSA) leading to the identification of 36 and 32 fragment hits binding Hel and MTase from DENV, respectively. In a second stage, we set up a fragment-based X-ray crystallographic screening (FBS-X) in order to provide both validated fragment hits and structural binding information. No fragment hit was confirmed for DENV Hel. In contrast, a total of seven fragments were identified as DENV MTase binders and structures of MTase-fragment hit complexes were solved at resolution at least 2.0Å or better. All fragment hits identified contain either a five- or six-membered aromatic ring or both, and three novel binding sites were located on the MTase. To further characterize the fragment hits identified by TSA and FBS-X, we performed enzymatic assays to assess their inhibition effect on the N7- and 2'-O-MTase enzymatic activities: five of these fragment hits inhibit at least one of the two activities with IC50 ranging from 180μM to 9mM. This work validates the FBS-X strategy for identifying new anti-flaviviral hits targeting MTase, while Hel might not be an amenable target for fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD). This approach proved to be a fast and efficient screening method for FBDD target validation and discovery of starting hits for the development of higher affinity molecules that bind to novel allosteric sites.
Organizational Affiliation:
Aix-Marseille Université, AFMB UMR 7257, 163 Avenue de Luminy, Case 932, 13288 Marseille Cedex 09, France; CNRS, AFMB UMR 7257, 163 Avenue de Luminy, Case 932, 13288 Marseille Cedex 09, France.