Protein Dimerization on a Phosphonated Calix[6]arene Disc.
Rennie, M.L., Doolan, A.M., Raston, C.L., Crowley, P.B.(2017) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56: 5517-5521
- PubMed: 28407337
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201701500
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
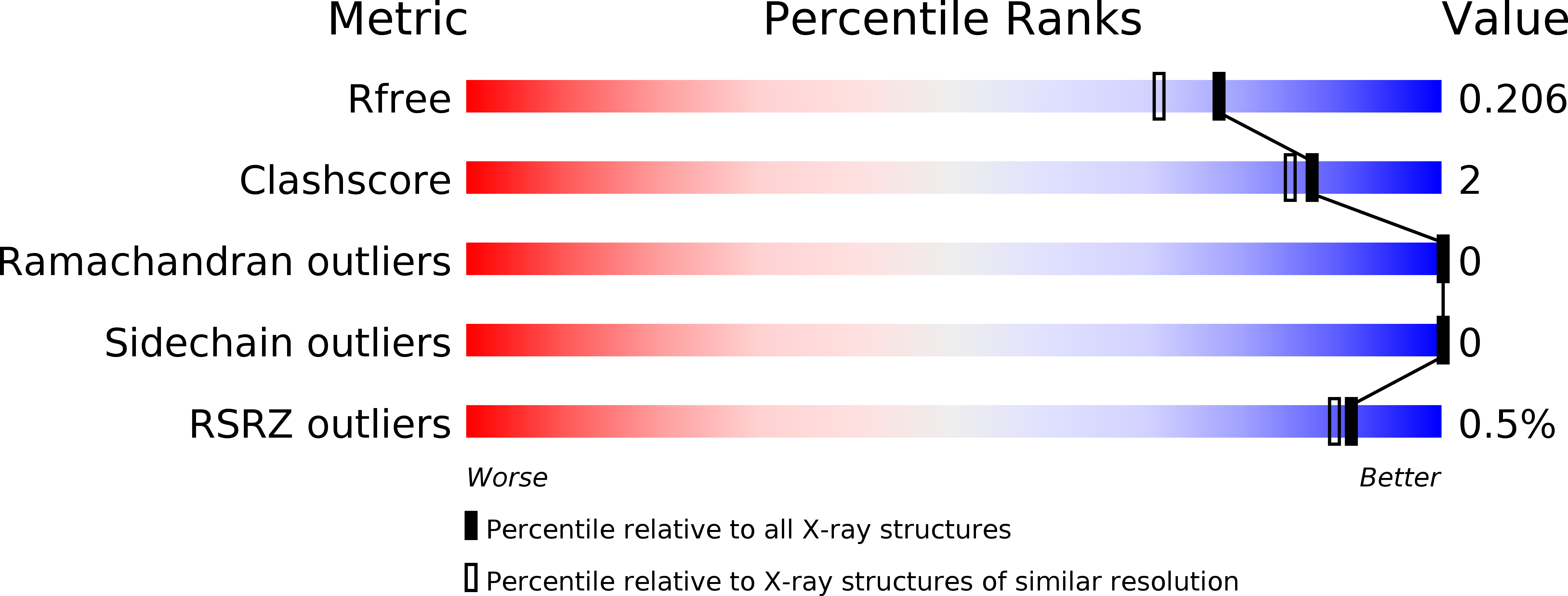
5LYC - PubMed Abstract:
Complex formation between cationic cytochrome c and the water-soluble, poly-anionic p-phosphonatocalix[6]arene (pclx 6 ) was investigated. A crystal structure (at 1.8 Å resolution) revealed a remarkable dimeric disc of pclx 6 that acts like glue to mediate a symmetric (C 2 ) protein dimer. The calixarene disc has a diameter of about 1.5 nm and masks about 360 Å 2 of protein surface. The key protein-calixarene contacts occur via two linchpin lysines, with additional contacts provided by a small hydrophobic patch. The protein-calixarene supramolecular assemblies were observed in solution by size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering and NMR spectroscopy. Using isothermal titration calorimetry and NMR data, an apparent K d in the low micromolar range was determined for the charge-rich protein-calixarene complex. In contrast to p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene, the larger pclx 6 has a single, well-defined binding site that mediates the assembly of cytochrome c in solution.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Chemistry, National University of Ireland Galway, University Road, Galway, Ireland.