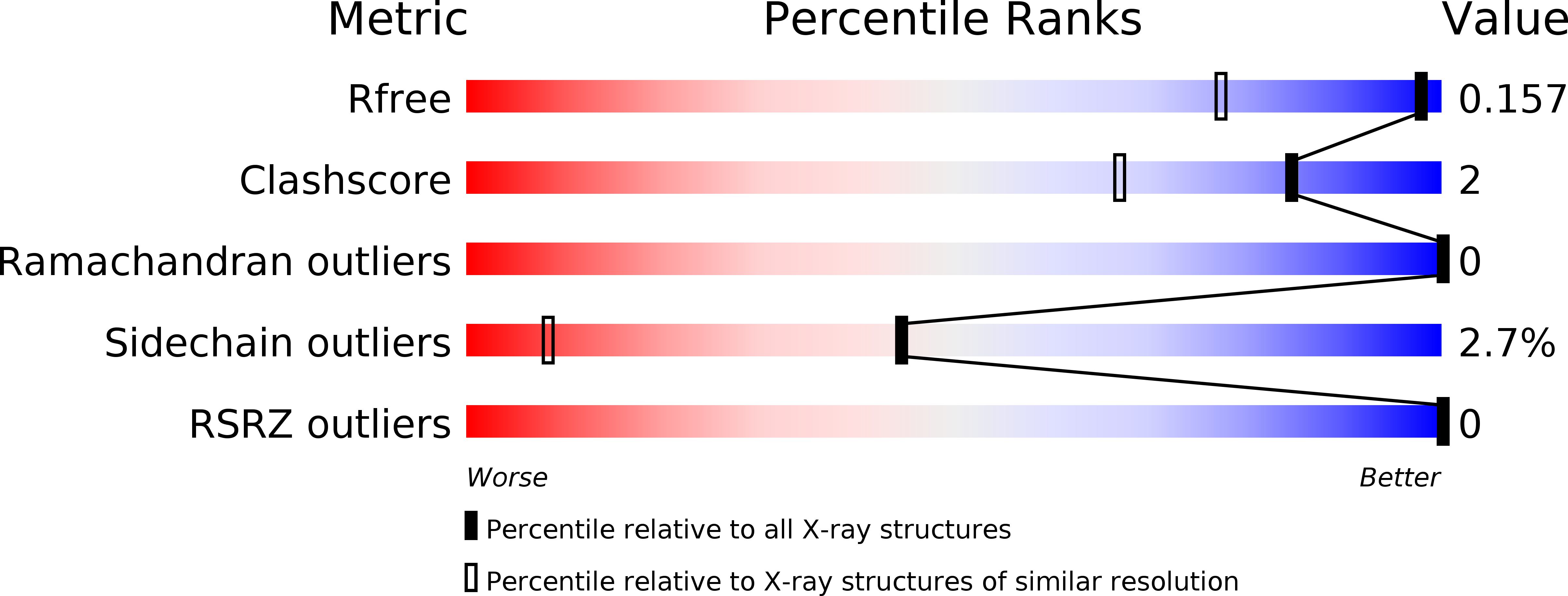
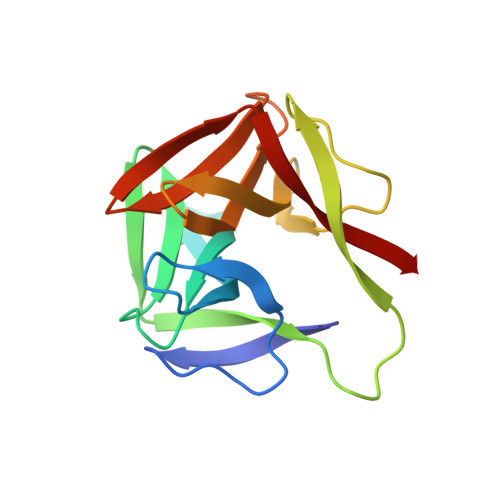
DM9 Domain Containing Protein Functions As a Pattern Recognition Receptor with Broad Microbial Recognition Spectrum.
Jiang, S., Wang, L., Huang, M., Jia, Z., Weinert, T., Warkentin, E., Liu, C., Song, X., Zhang, H., Witt, J., Qiu, L., Peng, G., Song, L.(2017) Front Immunol 8: 1607-1607
- PubMed: 29238341
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01607
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5MH0, 5MH1, 5MH2, 5MH3 - PubMed Abstract:
DM9 domain was first identified in Drosophila melanogaster , and it was subsequently found to integrate with or without other protein domains across a wide range of invertebrates and vertebrates. In the present study, a member of DM9 domain containing protein (DM9CP) family from marine invertebrate Crassostrea gigas (designated CgDM9CP-1), which was only composed of two DM9 domains, was taken as a protein model to study the biological functions of DM9 domain and its molecular determinants. CgDM9CP-1 was found to exhibit high binding specificity and avidity toward d-mannose residue. It served as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) with a broad range of recognition spectrum to various pathogen-associated molecular patterns, including lipopolysaccharide, peptidylglycan, mannan, and β-1, 3-glucan in a d-mannose-dependent manner, as well as bacteria and fungi. In order to reveal the molecular mechanism underlying its pattern recognition activity, the crystal structures of wild-type and loss-of-function mutants were solved, and Asp22 and Lys43 were found to be the critical residues for ligand recognition. Moreover, CgDM9CP-1 protein was found to mainly distribute on the surface of C. gigas hemocytes, and it could be translocated into cytoplasm and colocalized with the engulfed microbes during hemocyte phagocytosis. The present result clearly indicated that CgDM9CP-1 was a PRR, and it provided an important clue for the better understanding of DM9CP function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China.