Structural Study on the Reaction Mechanism of a Free Serine Kinase Involved in Cysteine Biosynthesis
Nagata, R., Fujihashi, M., Kawamura, H., Sato, T., Fujita, T., Atomi, H., Miki, K.(2017) ACS Chem Biol 12: 1514-1523
- PubMed: 28358477
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00064
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5X0B, 5X0E, 5X0F, 5X0G, 5X0J, 5X0K - PubMed Abstract:
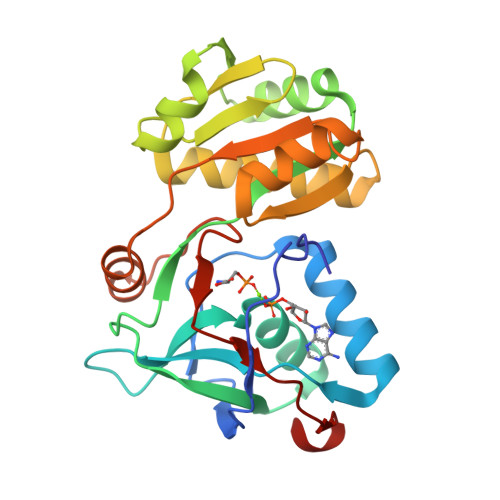
A free serine kinase (SerK) is involved in l-cysteine biosynthesis in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. The enzyme converts ADP and l-serine (Ser) into AMP and O-phospho-l-serine (Sep), which is a precursor of l-cysteine. SerK is the first identified enzyme that phosphorylates free serine, while serine/threonine protein kinases have been well studied. SerK displays low sequence similarities to known kinases, suggesting that its reaction mechanism is different from those of known kinases. Here, we determined the crystal structures of SerK from T. kodakarensis (Tk-SerK). The overall structure is divided into two domains. A large cleft is found between the two domains in the AMP complex and in the ADP complex. The cleft is closed in the ternary product complex (Sep, AMP, and Tk-SerK) and may also be in the ternary substrate complex (Ser, ADP, and Tk-SerK). The closure may reorient the carboxyl group of E30 near to the Oγ atom of Ser. The Oγ atom is considered to be deprotonated by E30 and to attack the β-phosphate of ADP to form Sep. The substantial decrease in the activity of the E30A mutant is consistent with this mechanism. Our structures also revealed the residues that contribute to the ligand binding. The conservation of these residues in uncharacterized proteins from bacteria may raise the possibility of the presence of free Ser kinases not only in archaea but also in bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University , Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan.