Structural insights into the committed step of bacterial phospholipid biosynthesis.
Li, Z., Tang, Y., Wu, Y., Zhao, S., Bao, J., Luo, Y., Li, D.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 1691-1691
- PubMed: 29167463
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01821-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XJ5, 5XJ6, 5XJ7, 5XJ8, 5XJ9 - PubMed Abstract:
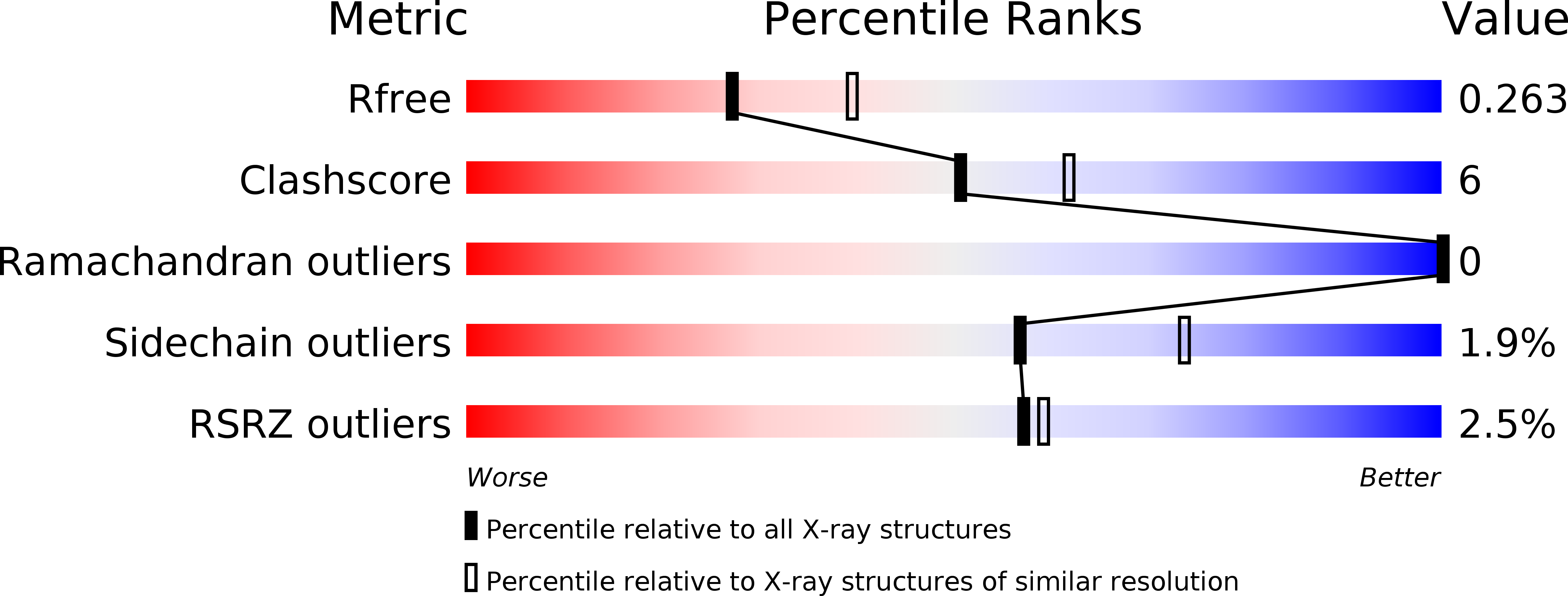
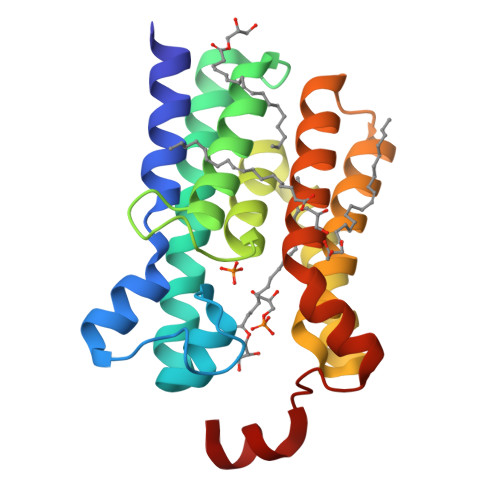
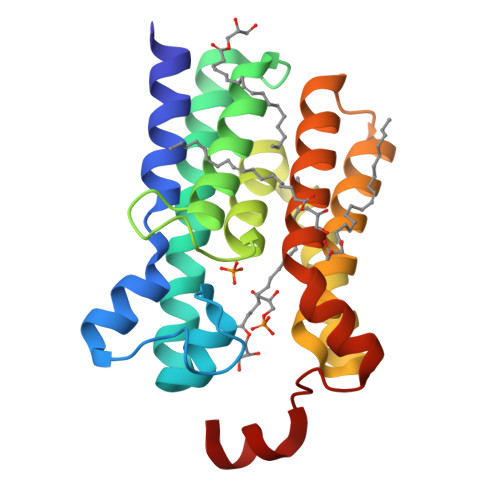
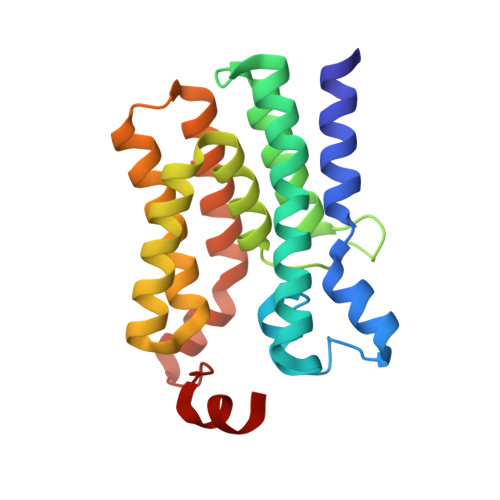
The membrane-integral glycerol 3-phosphate (G3P) acyltransferase PlsY catalyses the committed and essential step in bacterial phospholipid biosynthesis by acylation of G3P, forming lysophosphatidic acid. It contains no known acyltransferase motifs, lacks eukaryotic homologs, and uses the unusual acyl-phosphate as acyl donor, as opposed to acyl-CoA or acyl-carrier protein for other acyltransferases. Previous studies have identified several PlsY inhibitors as potential antimicrobials. Here we determine the crystal structure of PlsY at 1.48 Å resolution, revealing a seven-transmembrane helix fold. Four additional substrate- and product-bound structures uncover the atomic details of its relatively inflexible active site. Structure and mutagenesis suggest a different acylation mechanism of 'substrate-assisted catalysis' that, unlike other acyltransferases, does not require a proteinaceous catalytic base to complete. The structure data and a high-throughput enzymatic assay developed in this work should prove useful for virtual and experimental screening of inhibitors against this vital bacterial enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, Shanghai Science Research Center, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 333 Haike Road, Shanghai, 201210, China.